How to Plan and Launch an MVP: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Updated: Aug 27, 2024
- 8 min
Rolling out an MVP in software development is a crucial moment when building a startup. It’s your first chance to test your business idea in the real world.
But many founders skip doing enough research first. Sometimes, they don’t properly budget for developing their MVP.
Other times, founders don’t plan out a product launch strategy before releasing their MVP. You need to define what a product launch looks like first before setting your MVP loose.
So, how do you launch an MVP the right way?
In this ultimate guide, we’ll walk through the key steps for planning, building, and launching an MVP.
Let’s dive in!
Develop your MVP to validate a product-market fit with our expert software developers — contact us today to get started!
Understanding Product Launches
Product launch meaning refers to placing your MVP on the market. It means that you allow the first customers to try your product.
The launch of product comprises several important steps. It includes idea validation, development of UX prototypes, UI design, coding and marketing / sales activities.
Thus, product launch definition bases on implementation of the concept in the well-working platform. And then it goes through the whole cycle of creation, testing and learning business hypotheses.
There are several approaches to go-to-market strategy of an MVP launch.
Soft Launches
Soft launch meaning refers to the product release to the limited half of the target audience. The main idea of soft product launching is to reduce risks connected with product release.
The lean startup methodology calls these first customers the early adopters. Usually, every startup deals with early adopters to test the product concept before attracting the funds.
Soft launch strategy is based on a few key points. They are related to initial purpose of creating MVP:
- Receive the customers’ feedback. Collecting customer’s opinions helps to improve the usability and user journey. It also allows prioritizing hypotheses and features for the further development.
- Understand the customer willingness to pay.
- Test the monetization options. Soft launch helps to discover the viable monetization models, under which the customer would pay. Of course, only if monetization models are the part of business hypotheses to validate.
In fact, sometimes founders misinterpret the meaning of soft launch and MVP launch. There is an easy marker to differentiate these terms.
Soft launch is about market conditions to launch the product. Usually, it refers to a limited market niche or very specific audience, or geographical position.
An MVP launch is about the first iteration of the product. It includes the first version of user experience and specific scope of features.
Here’s everything you need to know about building a brand from scratch, from concept to execution.

Hard Launches
Let me be clear – a hard launch is not the best option for MVP launching.
The hard launch is a release of a ready-made product with a huge marketing activities to attract customers. This type of product launch is applicable to the mature products.
It’s a common framework for an enterprise business, that already passed through MVP and soft launch stages. The hard launch makes a good sense in case:
- you have a large and predictable audience.
- you have strong enough infrastructure.
- you can successfully anticipate the market reaction.
A good example of hard launch is a desktop or smartphone software update.
Thus, in battle of soft launch vs hard launch there are no winners and losers. The first one makes a big deal for startups, while the other one is good for the big and predictable businesses.
Dark Launches
The dark launch is a product launch methodology based on the process of continuous delivery. In simple words, it’s a regular feature update of your Minimum Viable Product.
Why is it called a “dark” one? Because you release a new feature for a small amount of users, who don’t know, that they are testers. This approach allows you to track the user behavior in real time. It’s a perfect way to decide, whether a new update is efficient enough to scale at all users.
For example, you have an idea of implementing a one-click payment service. You can start with 1% of your audience, then scale to 5% and then to 10% and so on. Live-time tracking helps you to analyze how changes impact the app performance.
Yet, a successful product is always a result of product planning and thorough analysis.
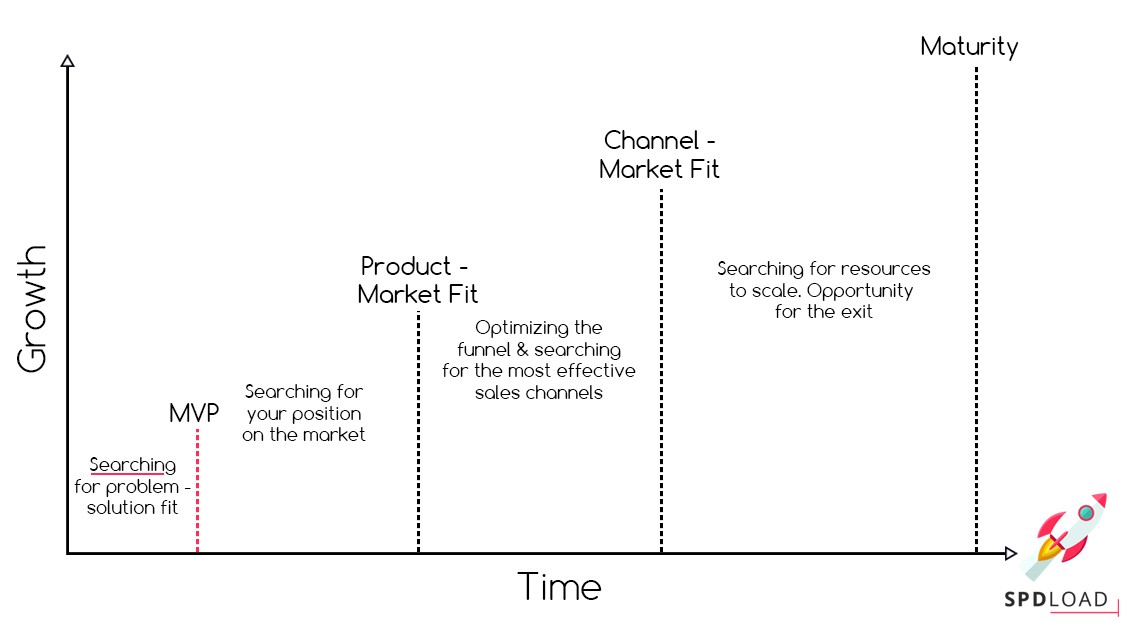
New Product Planning and Launch Process
Once the founder has decided to build a startup, he or she needs a product planning pattern to follow. It’s important to keep the whole process holistic, clear and systematic.
New product planning process focuses on a concept of the idea. It includes decisions and steps required to build a profitable application. In other words, founder as a product planner decides what and how would affect the final result.
In contrast to product planning, the launching strategy focuses on go-to-market activities. While a product plan is about feature list, a launch strategy is to choose the most relevant marketing campaign to attract the target audience.
There is a common misconception among many startup founders that a product planning is a one-time activity. But It has the same iterative character, as a development process.
Product planning is the flip side to an MVP launch. Both of these terms are interconnected. For example, the prioritization of features is directly related to market positioning and finding your advantages over competitors.
Thus, let’s clarify the step-by-step process of product planning and development.
5-Step Product Launch Checklist
- Generate and list your ideas. You will need the list of business hypotheses to track the dynamic of your MVP after launching. It helps to make the right decision. You can set up a limited number of features for every iteration to keep the process simple and effective. Use Lean Canvas as a launching framework.
- Keep the tempo of rapid changes. The main idea of being a startup and launch an MVP is moving fast-to-market. Startup has a privilege to change as many times as required. The founder needs to set up flexible and innovative culture to be agile.
- Set up SMART goals. These goals should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic and Timely. This complex helps you to move from one milestone to another without losing the focus.
- Focus on profit. A startup’s name, brand, logo or colors don’t mean much at the early stages of development. The profit is the only metric that shows viability of your product in the market.
- Always be customer-oriented. The main rule of a product launch is that your users should love your product, not you. To build a successful product you should work in collaboration with the users. If they have paid once, keep the strategy going and motivate them to get their friends to sign up too.
Tips for Successful Product Launches
- Don’t waste time on features. A Minimum Viable Product app is a basic idea or a model of your “ideal” product. You need it to test-run your idea within your target market. The only things that matter at this stage are the core features of your product. The secondary ones, along with some not major functions can be developed further down the line.
- Do not be afraid to try things. Speed should be your main priority when testing your solution in the market. Many founders wait until their product can fulfil every need at once. But this is not a necessity. And it is often impossible until you begin to truly understand your customers and their problems. That is why it is important to be able to react quickly to any changes both within the market and customer’s behavior.
- Do not build a money-burning MVP. An MVP launch requires the minimum set of features just to be able to solve one user’s problem. The truth is that 9 out of 10 startups fail. And it usually happens because the entrepreneurs burn money before even closer looking at the market’s reaction to their solution.
- Rush development. Progress is much more important than perfection. Product launch allows you to test how feature list changes and how the marketing activities are related to your target audience.
- Cut out anything that is not necessary. Iteration is the basic timeframe that is needed to develop a digital product. It is usually about 1-2 weeks. Iteration always includes new features and business hypotheses. Thus, it helps you to identify the most efficient tactics in a short period of time. And to cut off all the unnecessary things.
8 Key Product Performance Metrics
Digital products require a permanent measurement of success. The numbers are the best markers. However, the only real identifier of your success is how customers love what you offer:
- The traffic of the app. The most important metrics is the number of people who want to use your solution. The more visitors you have, the higher your chances of getting users.
- Use free tools like SimilarWeb to find out the traffic of your platform. In case your budget allows, you can also use Ahrefs.
- When talking about a mobile app, the best way to check it is Google Play or Apple Store statistics.
- The number of registrations. The main approach is to identify your customers and the general flow of visitors on the site. This is your strongest indicator whether customers are interested in your business model.
- The number of active users. This is the only thing that shows the real level of interest in your product. The next challenge is to find out how to keep those customers interested enough to keep coming back.
- User engagement. This parameter shows the behavior of your customers. Identify what is the most important indicator for your solution and then track it. To do this you can use such apps as Amplitude or Mixpanel:
- Look at YouTube or Instagram – the key indicator for both of them is the time spent on the platform.
- For Uber-like app it would be the number of rides taken.
- The number of paying users. If your business model doesn’t generate revenue – it is useless. In case this number is low, it is time to make a pivot and develop another business model.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC). This shows the correlation between the amount of money spent and the number of customers. The lower this number, the easier it is to grow:
- Facebook Ad company costs 100 dollars, but you get only 5 new customers, that means CAC is 20 dollars. This CAC calculator simplifies tracking your marketing efficiency and budget allocation.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV). This parameter shows how much revenue a startup can expect from a particular customer throughout the time of using an app. The longer the customer makes purchases, the higher that rate is. The relevance between CLV and CAC shows how much money the product generates.
- Churn rate. This value is critically important for subscriber-based business models, as it shows how many customers stop using the product. If they do not stay long enough to at least pay off the CAC, then you are facing a big problem and should consider making a pivot. Tracking customer retention is essential, and this churn rate calculator can help measure your customer loyalty.
From concept to creation – launch your marketplace with SPDLoad!
Ready to Develop Your Own MVP?
If you feel you need more support getting your first MVP off the ground, consider partnering with an experienced development team.
Our MVP builders can guide you through the validation, planning, and execution process. We can set your product (and your startup) up for a successful launch and continued refinement after release.
Get in touch to learn more about our end-to-end MVP development and product launch services.
Now is the time to start testing and improving your big ideas with real users in your target market. We’re here to collaborate and make that happen quickly and affordably.
Planning your own business? Here are essential business startup tips to guide you.