5 Innovative FinTech Business Models (+Real Examples)
- Updated: Aug 27, 2024
- 11 min
Fintech continues to disrupt traditional financial services with new innovations and business models.
From cost savings to better service, the benefits of fintech are transforming industries.
Over the past decade, fintech startups have unleashed a wave of creativity, leveraging emerging technologies and meeting evolving consumer needs.
In this article, we will discuss five innovative fintech business models that are making a significant impact today.
We will explain how each model works and its unique value proposition and provide examples of companies implementing these approaches in the real world.
If you are thinking about creating your own fintech app, feel free to dive into fintech app development to see what it takes to create a standout financial app.
Unlock your startup potential now — start transforming your vision into a scalable solution today!
Understanding FinTech Business Models
FinTech, a sector with about 26,000 active startups innovating financial technology solutions, is gradually getting competitive as more fintech startups emerge.
The financial expectations of the sector’s service users are also expanding; thus, newbies need to adopt an innovative business model to thrive.
What is a FinTech Business Model?
A FinTech business model is a plan for a financial technology business; this includes operating strategy, revenue sources, and intended customer base.
FinTech organizations generally adopt inclusive approaches to finance, enabling consumers to have apt access to a wide range of financial services and products.
Furthermore, these services and products are available across mobile devices and don’t require a convoluted sign-up process. So, what determines a suitable business model?
Factors that Determine the Right Business Model for Your Startup
Before choosing a FinTech operation model that can complement your startups’ goal, it’s sacrosanct that you first highlight the following factors.
After which, you should opt for a business model that aligns with them.
| Factors | Description |
| Startup’s goal | What are the goals and objectives for establishing your startup? |
| Specific audience | What specific audience are you interested in developing a product for? Your answer should guide the business model to use. |
| Business processes | Before launching your product, you need to understand the core aspect of your business offerings and determine key operational processes. |
| Key partners | Consult with investors, co-founders, and other strategic alliances. |
| Consumer demand | The thriving need in your geographical target market should guide your FinTech adoption model. |
Now that you’re acquainted with what a business model is, and the factors to consider before choosing one.
Let’s go into a detailed discussion on the most prominent FinTech business models. 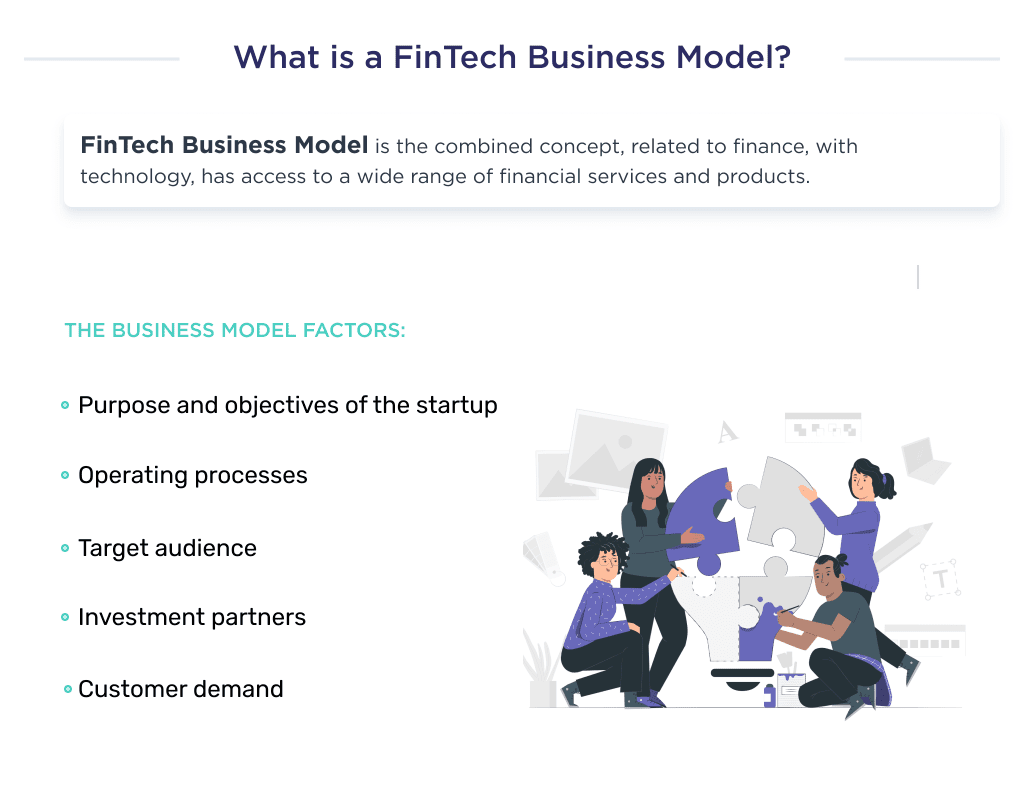
Most Prominent FinTech Business Models
As entrepreneurs, founders, and investors strive to synthesize revolutionary ideas for fintech startups, the list of 5 FinTech business models below can help to point out a suitable direction for your startup’s product.
1. Alternative Credit Scoring
An alternative credit score is a FinTech creation that helps borrowers determine lenders’ creditworthiness by using relatable, current, and easily available data such as their digital footprint.
This business model is valuable for FinTech companies willing to issue loans to individuals not properly captured by the traditional credit score system.
E.g., small business owners or private loans for college.
As a startup, you can request a wide range of alternative data and synchronize the result alongside some traditional records for a robust credit assessment.
Many FinTech companies are already using this FinTech business model in their financial product by loan lending app development, with some noteworthy examples being: Nova Credit, Canopy, Cortera, etc.
Why You Should Own a Lending Platform that uses Alternative Credit Score Model
Here are some statistics suggesting that adopting an alternative credit score model would be an intelligent business move;
- As of October 2020, it’s reported that as many as 45.1 percent of U.S.-based black consumers had subprime credit scores.
- One out of ten Americans is considered to be “credit invisible.”
Owning a lending platform ranks among the most profitable ventures in the globe. However, for noteworthy profit, the statistics above show that it’s best to adopt an alternative credit scoring model as it helps to capture a greater audience pool.
Pros and Cons of Alternative Credit Score
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
Now that you have a concise idea of the intricacies of the alternative credit score business model let’s take a look at another FinTech business model. 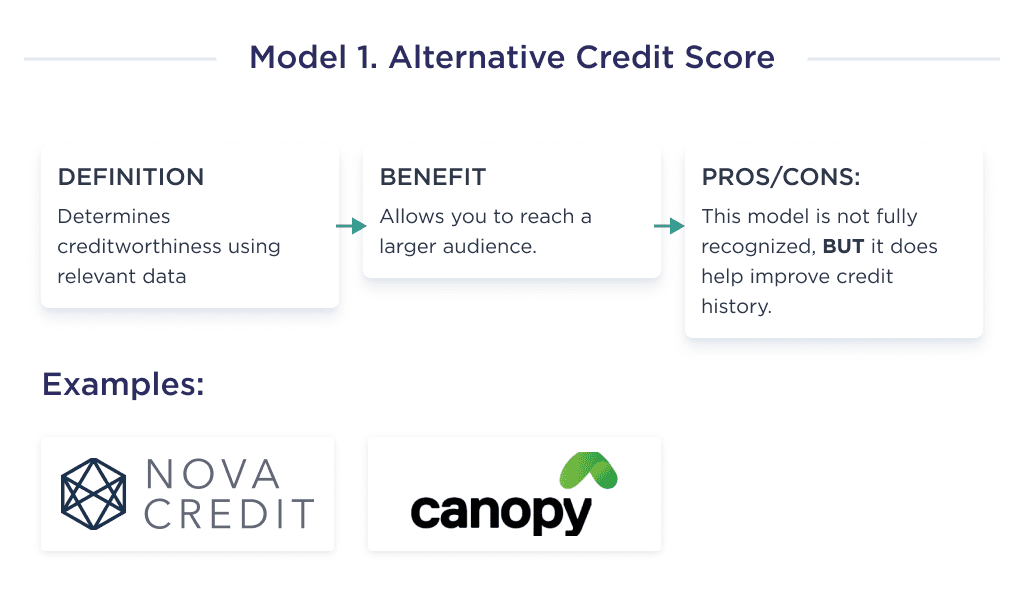
2. Alternative Insurance Underwriting
Traditional insurance underwriting determines insurance premiums based on some predetermined quantifiable factors. But, those components are often termed un-encompassing enough as they don’t capture non-quantifiable but important factors like exercising.
Let’s take, for example, two individuals of the same weight and height who don’t take alcohol and are non-smokers will likely get the same insurance policy value. However, one may be an exercise freak while the other spends most of his day on the couch, increasing his risk of diabetes.
To help capture an intending policy holder’s risk more effectively, alternative insurance underwriting captures both quantifiable and unquantifiable data like medical history, lifestyle, social signals.
Combined with self-learning and intelligent algorithms, Insurtech startups and insurance companies now have a smarter way to choose policyholders, provide better terms and conditions, and offer alternative payment options.
Some FinTech startups using this model to take a cue from include: Next Insurance, Clover Health, etc. If you are interested in learning more about the insurance industry, see 15 examples of insurance companies we explore in our recent guide.
For insurance companies looking to innovate, car insurance app development is a game-changer in customer engagement.
Why you Should Use this Model
As a startup with a penchant for quick growth, it’s imperative to adopt a business model that appropriately exemplifies your developmental strategy as a business.
By using this operation model, there’s a guarantee that you’ll appropriately weigh all scenarios and give policyholders the premium that they truly deserve.
Doing this, in turn, leads to a top-notch user experience and a high customer retention rate.
Customers will get premiums they feel that they truly deserve.
Crafting Custom Mobile Apps That Delight Users!
Pros and Cons of Alternative Insurance Underwriting
Before adopting this model, carefully weigh its pros and cons vis-a-vis a traditional alternative insurance underwriting.
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
Now that you have a fairer understanding of alternative insurance underwriting, let’s dig into another FinTech business model. 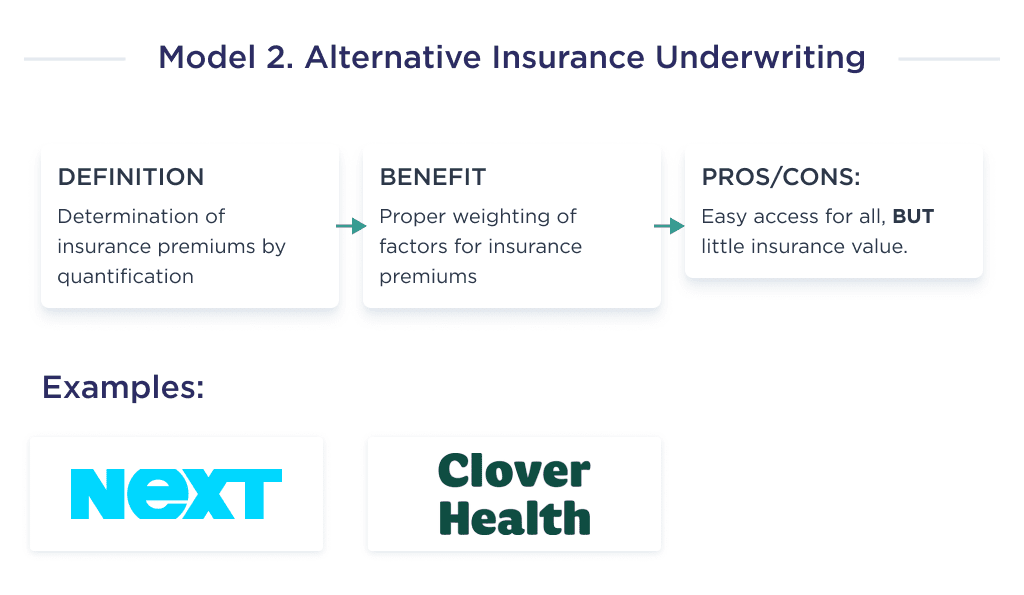
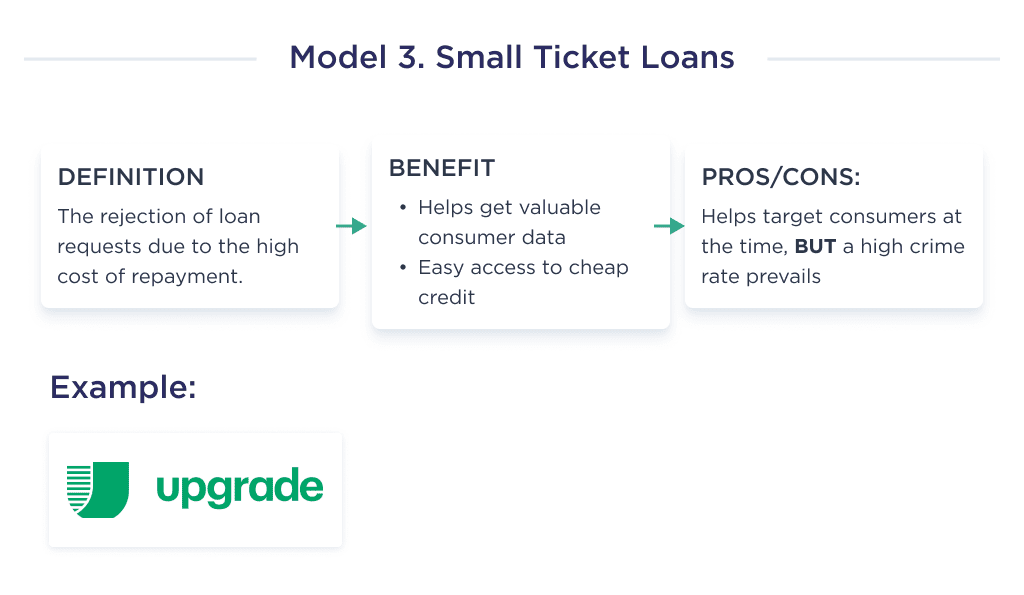
3. Small Dollar Loans
It’s a common phenomenon to see banks and lenders reject applications for small-ticket loans due to its low margins and its relatively high cost of setting up and recovering those loans.
However, some FinTech companies adopt a business model that allows them to cater to this target market’s needs.
Some FinTech lending startups have crafted an effective impulse buy mechanism strategy.
This is a one-click buy now button that is placed on e-commerce websites to allow customers to make quick purchases through consumer loans without a need to enter their credit card details or some form of authentication.
These loans are often underwritten at a 0% interest, and consumers are given an option to make payments in scheduled installments.
As a startup interested in this business model, you can earn some profit by opting to request interest on your loans or by sharing customers’ data with the original equipment manufacturers.
An example of a FinTech company thriving with this business model is Upgrade.
Why you Should Use this Model
Like every other model mentioned above, this strategy helps you target the market most traditional lenders shy away from exploring.
This business operating model is very easy for businesses to adopt as they’ll be getting valuable consumer data from your FinTech startup.
At the same time, consumers also enjoy easy access to cheap credit.
Pros and Cons of Small Ticket Loans
Here is a tabular depiction of the pros and cons of this method;
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
4. Investment Management
Most consumers find it challenging to make investments and keep track of their assets accounts.
As a startup, you can take advantage of this business model by creating a wealth management platform that’ll enable investors to trade seamlessly from any location.
Trades are executed on an intuitively built trading application, and signals are sent to high-frequency traders that can influence asset prices.
Investors’ positions are executed instantaneously, and asset liquidation is carried out within a short duration.
Prominent examples of successful FinTech startups with this new business model are Robinhood, eToro, Betterment, etc.
Why you Should Use this Model
Check out these statistics that suggest why you should use this model in the financial sector;
- A recent study by Gallup shows that about 56% of the U.S. population invests in stocks, while a significant proportion of them are active traders.
- Similar research conducted by the University of Chicago suggests that more than 16% of Americans invest in cryptocurrencies.
There’s no doubt that this FinTech business model will witness significant growth in the years to come.
Owning an investment solution puts your business in a perfect position to make noteworthy gains from the demand that’s poised to come.
To be profitable with this business model, your business may charge a profit for executed trades.
If you’re looking to build a stock trading platform, our article on how to build a stock trading platform covers all the key aspects.
Pros and Cons of the Investment Business Model
Like any FinTech model, it also has its pros and cons to consider. Here are two distinct ones.
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
With the concise information we’ve detailed above, you now have an idea of what it takes to build an investment application. Let’s discuss another FinTech business model. 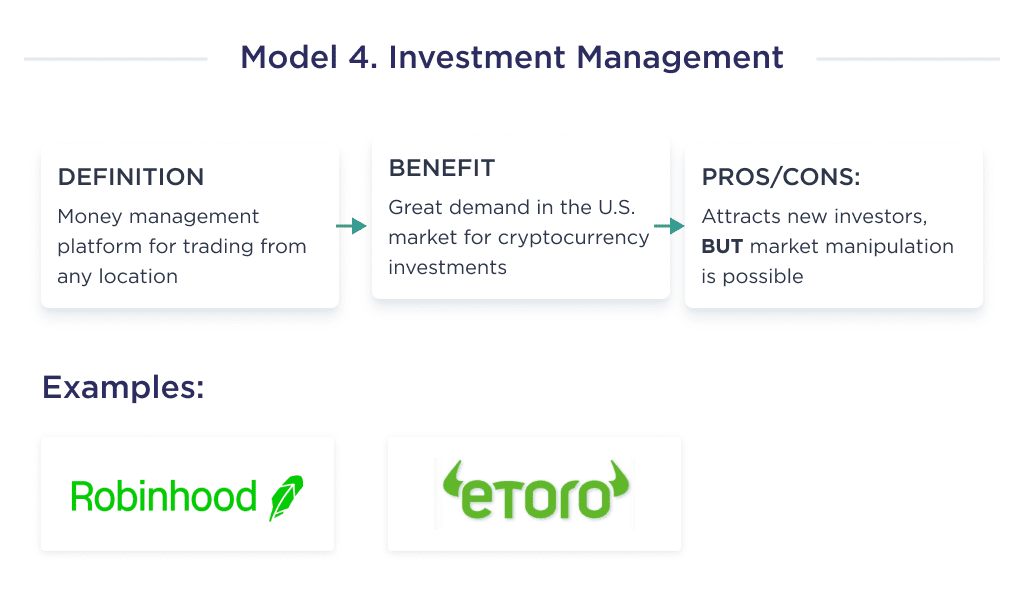
5. Digital Banking
This business model encompasses web-based services and a high level of automation that may include generating and integrating APIs that enable cross-institutional service for delivering banking services and financial transactions.
With this FinTech business model, users can now access financial data, initiate money transfers through mobile, smartphone, desktop, and ATM devices, and make payments via debit cards.
Some examples of FinTech using this initiative in the financial services industry are Alliant, Revolut, TransferWise, Venmo, PayPal, Stripe.
Wondering how to accept card payments on your website? Check out our guide on how to accept card payment on-site for all the details.
Why you Should Adopt a Digital Banking Business Model
There are multiple reasons to adopt this business model in the FinTech industry. However, let’s first consider some verifiable statistical pieces of evidence:
- 78% of Americans use at least one digital banking product
- Over 80 million people in Europe will use neobanks.
- 31% of the world population is unbanked.
From the statistical evidence above, it’s logical to conclude that digital banks have wide acceptance amongst consumers.
However, over 31% of the population is without a bank account.
With a digital bank, you can easily advertise yourself to those already acquainted with an online bank and the unbanked.
Include blockchain technology in your product to help you create a more secure ecosystem for your consumer base, thereby giving you an edge over other financial institutions.
Pros and Cons of Digital Banking Business Model
Here are some pros and cons to appropriately consider before opting for this business model;
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
With the apt understanding of the FinTech operating models you now have, let’s discuss some examples of small businesses that have adopted these models in the FinTech market. 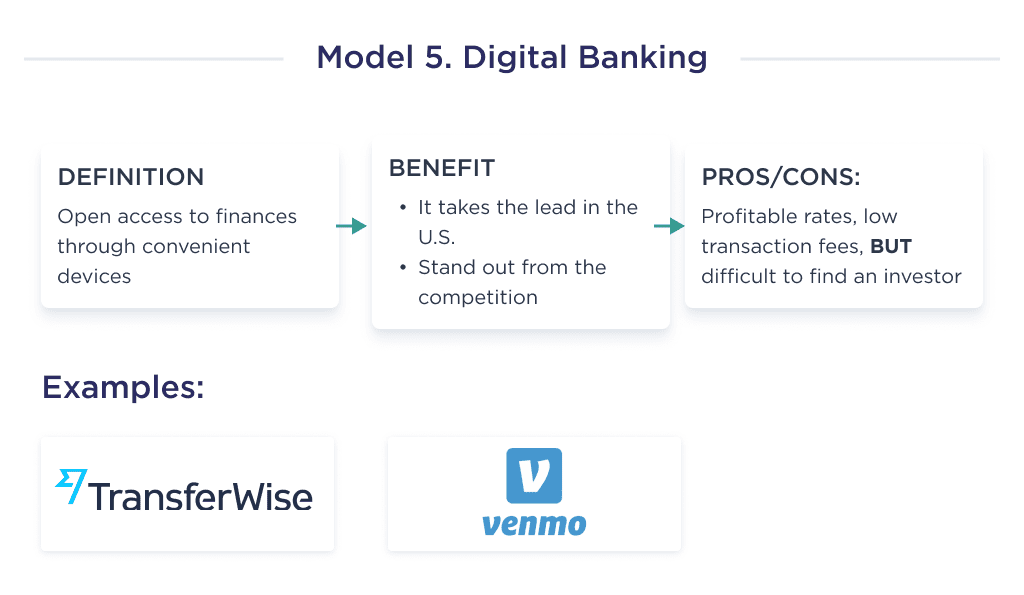
FinTech Startup Business Models – 3 Real-World Examples
Some well-known startups such as Rupeek, Solarisbank, and Revolut are examples of FinTech companies thriving by adopting one or some of the business operating methods above. Read on!
Revolut’s Business Model
Revolut is a digital banking platform that builds a fair and frictionless platform for making transactions and managing money worldwide.
Essentially, it acts as bank alternatives for both businesses and people.
Revolut offers cost-effective international funds transfers and free global spending at the interbank exchange rate to attract a large customer base.
Another unique selling point for this FinTech is that users can easily open an account within 60 seconds.
Revolut also supports the use of crypto such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, etc. on its platform.
If you’re wondering how to buy cryptocurrency in Australia, you’ll be pleased to know that Revolut allows its users to trade and invest in various cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin and Ethereum, on its platform.
Find the best TypeScript developers for your project.
How Revolut Makes Money
This platform makes money by collecting interest on loans issued.
The interest fee it charges depends on the customers’ credit score, loan sum, and length loan. An overdraft fee is also charged on late payments.
What to Learn From Revolut
Revolut understood that it was an underdog compared to traditional banks when it started operating; thus, the startup offered prospective users incentives such as feeless transaction, top-notch exchange rate, and fast account opening process. 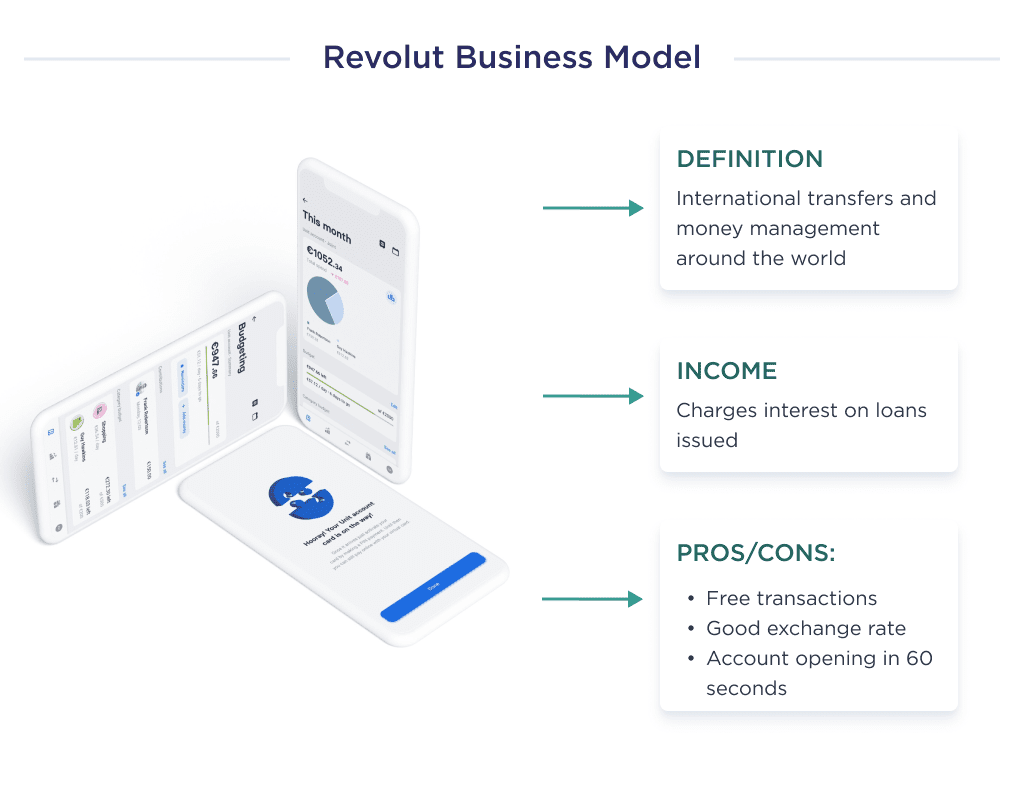
Solarisbank’s Business Model
Solarisbank is a German banking-licensed technology company that generates APIs for other FinTech products.
This FinTech service provider has mastered the technical and regulatory complexities of banking to deliver an apt user experience.
Solaris is quite distinct from other digital banks as they only offer APIs to innovators in need of trustworthy partnerships for online banking platforms, payment systems, and payment gateways while moving away from online payment application development partners
How Solarisbank Make Money
Solarisbank gets its revenue from its clients as they pay to make use of the startup’s APIs. The tech giant also collects interchange fees on card transactions.
What to Learn from Solarisbank
Due to the over-saturation of the B2C banking space, the company decided to create solutions that can empower prospective digital banking to function with ease. 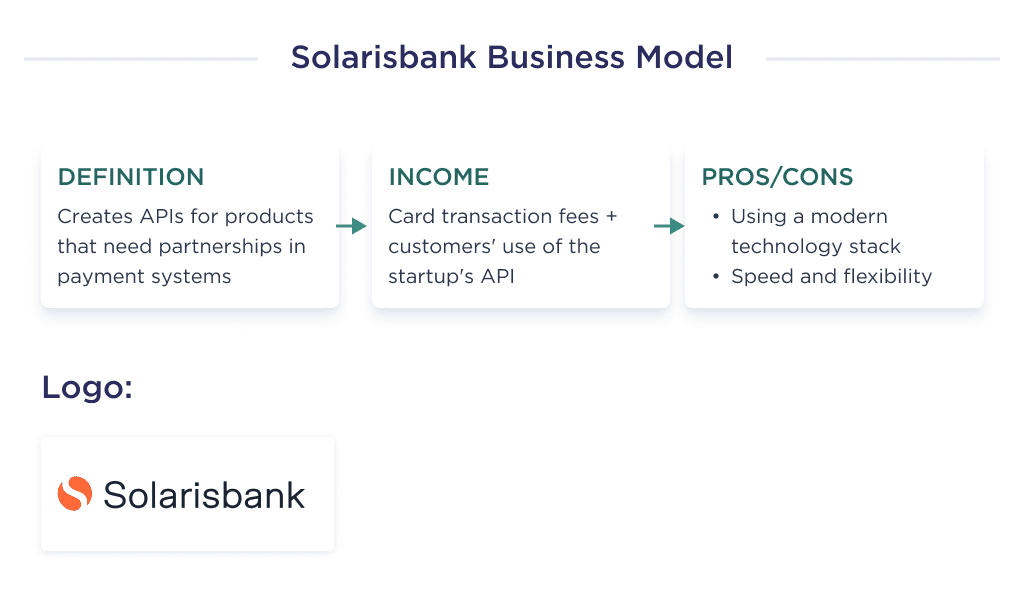
Rupeek’s Business Model
Rupeek is India’s foremost asset-backed lending platform. The platform helps Indians access credit most fairly and conveniently possible. The company recently made the news for pioneering innovative solutions that can be instrumental in monetizing India’s $2 trillion gold.
How Rupeek Make Money
Rupeek makes money from the interest it charges on its loan. Due to its strategy of reducing its overall cost, they offer interest at the best rate obtainable.
What to Learn from Rupeek
Rupeek gives consumers gold loans at the doorstep to complete the loan underwriting-to-disbursal process in less than an hour. This innovation puts the company in a niche of its own. 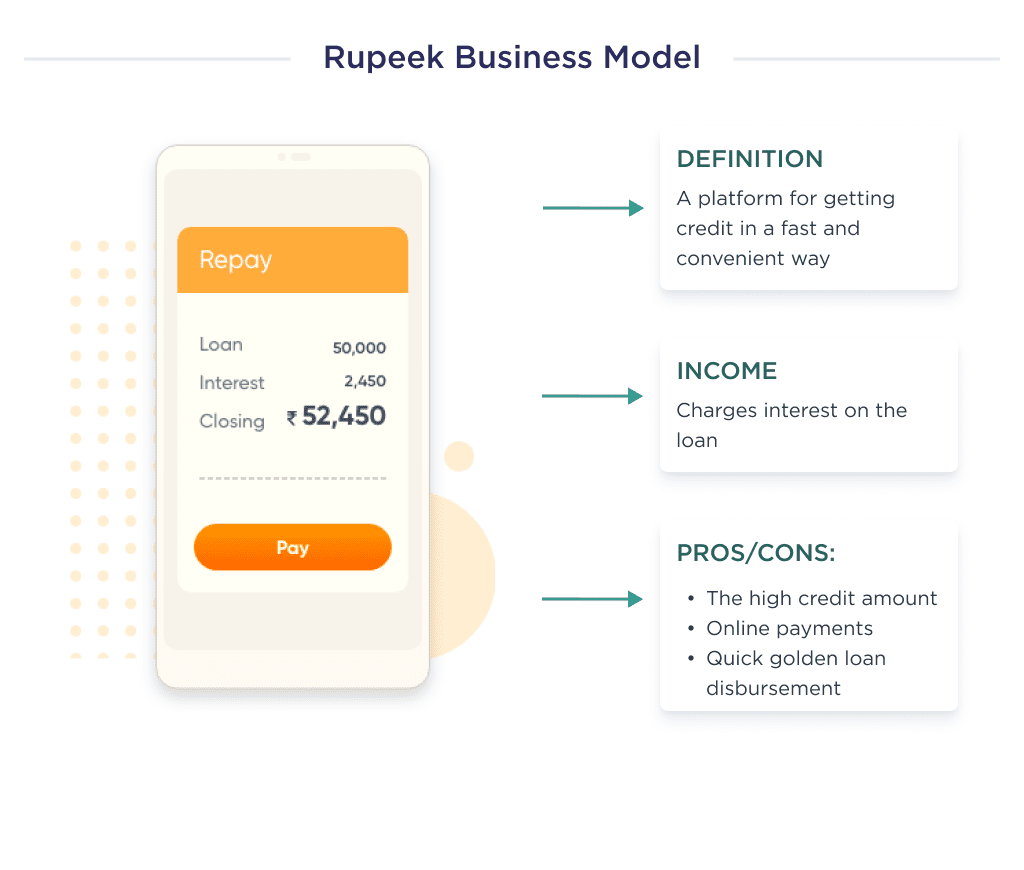
Turn FinTech Ideas Into Reality
As we explored, many innovative FinTech business models are disrupting finance. But an idea needs the right execution.
Our engineers and designers have decades of experience building digital financial products for major banks, startups, and more.
We can guide you from idea validation to launch and beyond:
- Architecting scalable cloud platforms
- Integrating financial data sources
- Ensuring banking-grade security
- Crafting intuitive user experiences
- Launching an MVP to validate your concepts
Contact us today if you have a promising FinTech model needing expert implementation. Our team is ready to turn your vision into reality.