19 Key Cybersecurity Trends
- Updated: Nov 10, 2024
- 7 min
As the digital world continues to advance, so do the threats that come with it.
Cybersecurity remains a major concern for individuals, businesses, and governments across the United States in 2025. Innovative and robust security measures are necessary to combat the increasingly sophisticated nature of cyber attacks.
This article dives into the 19 most critical cybersecurity trends, offering insights into how to safeguard digital assets in an ever-connected world.
Curious about where app development is headed? Our application development trends guide has the answers.
Transform your ideas into reality with top-tier software developers — contact us to get started!
Top Cybersecurity Statistics for 2025
- Cybercrime costs are expected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by the end of 2025.
- In 2023, 72.7% of all organizations worldwide fell prey to a ransomware attack.
- 75% of security professionals have observed increased cyberattacks over the past year.
- The global average cost of a data breach in 2023 was $4.45 million, a 15% increase over three years.
- Cyber insurance premiums in the US surged 50% in 2022, reaching $7.2 billion in premiums collected from policies written by insurers.
- For the 12th year in a row, the United States has the highest cost of a data breach at $5.09M.
1. Zero Trust Architecture
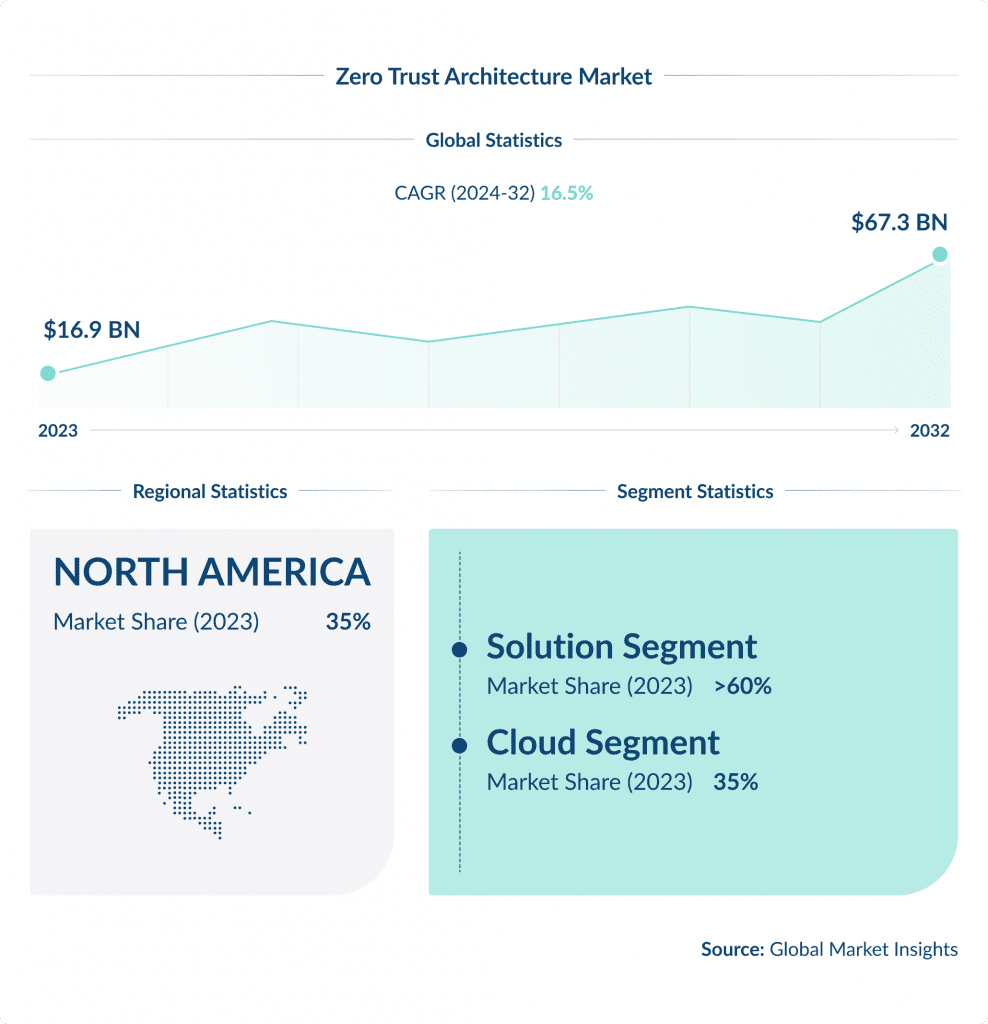
Zero Trust Architecture is a cybersecurity approach that revolves around the idea that organizations should not blindly trust anything or anyone – both within and outside their perimeters.
To ensure maximum security, they must verify and authenticate every system, device, or user attempting to connect to their networks before granting access.
With the increasing sophistication and frequency of cyber threats, adopting Zero Trust Architecture is no longer a luxury but a necessity.
According to a recent report by Forrester, about 60% of organizations are expected to implement Zero Trust capabilities by 2025, up from a mere 15% in 2020.
This approach helps minimize the attack surface, reduces the impact of potential breaches, and strengthens overall security by implementing strict access control and eliminating the notion of trust based on network location.
Learn about effective bot attack prevention strategies to safeguard your site and data.
2. Cloud Workload Protection
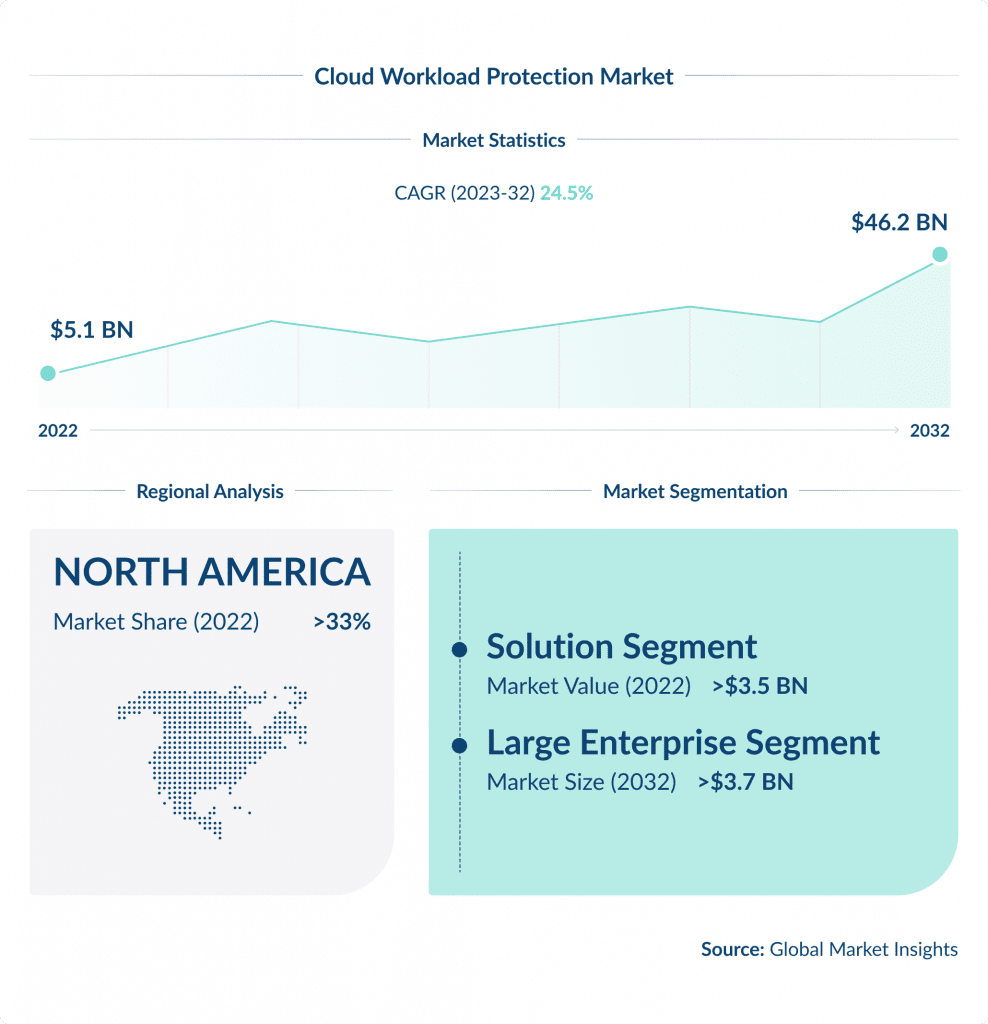
Cloud Workload Protection platforms are specifically designed to secure cloud environments, including the data, applications, and services in them.
As businesses increasingly move their operations to the cloud, robust cloud workload protection becomes critical.
It is anticipated that by 2025, over 45% of IT spending on system infrastructure, infrastructure software, application software, and business process outsourcing will shift from traditional solutions to the cloud, as per Gartner.
Cloud Workload Protection solutions provide comprehensive security for multi-cloud environments, ensuring data integrity, preventing data breaches, and complying with regulatory requirements through advanced security features like system hardening, vulnerability management, and runtime protection.
By choosing cloud-based app development, companies can ensure their applications are accessible and scalable.
3. Advanced Persistent Threats
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) are sophisticated cyber attack campaigns that target specific organizations or nations for espionage, data theft, or financial gain.
These campaigns are characterized by their stealth, persistence, and significant resources, often attributed to state-sponsored or highly organized cybercriminal groups.
The frequency and complexity of APTs are on the rise, as indicated by a report by Mandiant, which noted a 200% increase in identified APT groups over the past three years.
Organizations are responding by enhancing their threat detection and response capabilities, utilizing AI and machine learning for early detection, and adopting comprehensive cybersecurity frameworks to mitigate the risk posed by these threats.
From concept to creation – launch your marketplace with SPDLoad!
4. Breach and Attack Simulation
Breach and Attack Simulation (BAS) technologies enable organizations to simulate various cyber attacks against their IT infrastructure continuously and safely.
This helps them identify vulnerabilities and security gaps before hackers exploit them.
According to MarketsandMarkets, the BAS market size in the US is expected to grow from USD 218 million in 2020 to USD 1.7 billion by 2025 at a CAGR of 40.2% during the forecast period.
BAS tools automate the vulnerability assessment process, reducing the time and resources required for manual penetration testing.
This enhances overall security posture and enables organizations to focus on other crucial areas of their operations.
5. Securing APIs
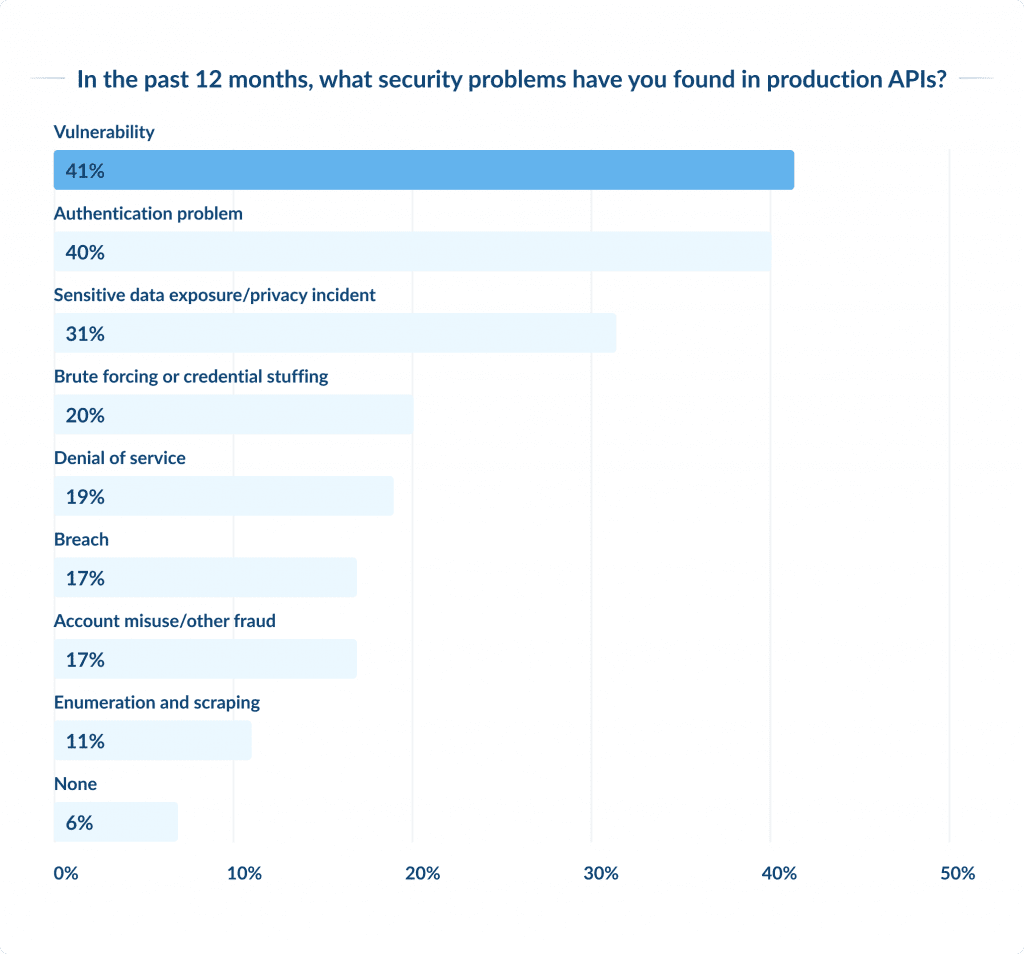
Ensuring the safety of APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) is critical, as APIs serve as the foundation of modern software development, facilitating communication and data sharing between various systems and applications.
With the widespread use of APIs, their security has become increasingly important, as vulnerable APIs are a prime target for attackers.
According to Gartner’s predictions, API abuses will become the most common attack vector by 2023, leading to data breaches in enterprise web applications.
6. Cyber-Physical Systems Security
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) are a bunch of technologies that integrate physical processes with software-based control systems. Examples include industrial control systems, smart grids, and autonomous vehicles.
As these systems become more interconnected, the potential impact of cyberattacks grows, affecting not just information systems but also physical infrastructure.
It’s essential to have a comprehensive cybersecurity framework for CPS to address unique challenges such as real-time constraints and safety-critical functions.
Ensuring CPS security requires a multi-layered approach, including securing hardware components, employing real-time threat detection algorithms, and fostering collaboration between IT and operational technology (OT) teams.
7. DevSecOps Practices
DevSecOps is a process that integrates security practices within the DevOps framework.
It promotes a ‘security as code’ culture and encourages flexible collaboration between release engineers and security teams.
DevSecOps bridges the gap between IT and security, ensuring speedy and secure code delivery.
The projected growth of the DevSecOps market is remarkable, and it is expected to reach USD 5.9 billion by 2023, with a CAGR of 31.2%, according to MarketsandMarkets.
Check out our DevOps services to learn more about our DevOps practices and tools.
9. SOAR/XDR Automation
Automating the identification, investigation, and resolution of cybersecurity incidents has become increasingly important for organizations.
SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) and XDR (Extended Detection and Response) technologies offer a great solution but without proper tuning this can lead to alert fatigue explained, where an abundance of low-value alerts desensitizes teams and dilutes response effectiveness.
SOAR tools are designed to integrate with various security solutions and automate responses to threats, thereby improving efficiency and reducing response times.
XDR goes beyond traditional endpoint detection and response (EDR) by integrating data from multiple security layers for deeper analysis.
By working together, SOAR and XDR provide a unified approach to threat detection and response, which results in comprehensive visibility across an organization’s security infrastructure.
According to Gartner, the adoption of SOAR tools is expected to increase from 5% in 2020 to 30% by 2025.
10. 5G and IoT Security
As the world is gearing up for the rollout of 5G technology, it is expected to speed up the adoption of IoT (Internet of Things) by offering faster and more reliable connections to devices.
However, this growth also poses new security challenges, as the growing number of connected devices expands the attack surface for cyber threats.
Securing 5G and IoT requires addressing vulnerabilities in device firmware, implementing robust network security measures, and adopting end-to-end encryption for data in transit and at rest.
According to the International Data Corporation (IDC), worldwide spending on IoT security is expected to reach $6 billion by 2023, underscoring the importance of investing in secure IoT frameworks.
12. Cyber Insurance
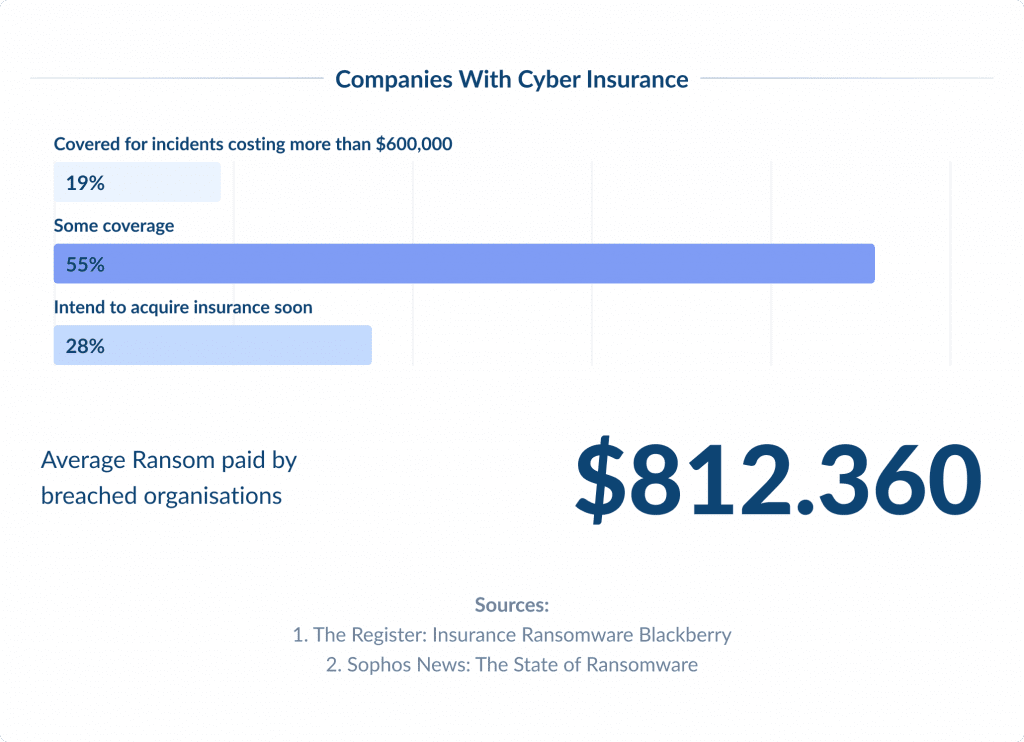
Cyber Insurance is quickly becoming an important part of risk management strategies for businesses in the US.
As cyber threats get more complicated and cause greater impact, companies are turning to cyber insurance to mitigate financial risks associated with data breaches, ransomware attacks, and other cyber incidents.
According to Statista, the global cyber insurance market is expected to reach $22 billion by 2025.
The policies generally cover expenses related to incident investigation, data breach notifications, loss recovery, legal fees, and sometimes, ransom payments.
However, insurers also emphasize the importance of strong cybersecurity practices as a prerequisite for coverage, urging businesses to bolster their security measures.
13. Supply Chain Risk Management
Supply chain risk management in cybersecurity has become increasingly important due to the interconnectivity of supplier networks.
Cyber attackers often target vulnerabilities within the supply chain to gain access to confidential information or disrupt business operations.
The recent SolarWinds attack brought attention to the potential scale and complexity of supply chain attacks, leading to a reevaluation of security practices.
Nowadays, companies prioritize the security of their supply chains through comprehensive risk assessments, continuous monitoring, and the implementation of secure design principles.
Effective management also includes enforcing strict cybersecurity standards and practices among suppliers.
14. Cyber Threat Intelligence
Understanding and analyzing emerging or existing cyber threats and actors is what Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) is all about. By doing so, we can prevent or mitigate cyberattacks.
Organizations use CTI to gain insights into adversaries’ tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), enabling proactive defense measures.
The market for CTI is projected to grow significantly, with Statista estimating it to reach $11.6 billion by 2023.
15. Cybersecurity Skills Shortage
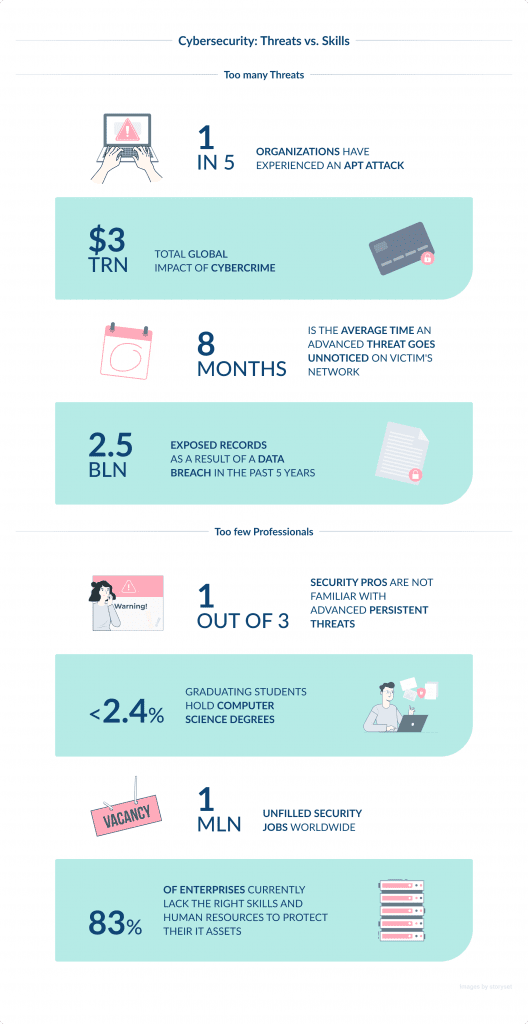
The shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals is a pressing issue in the industry.
Despite the increasing frequency of cyber threats, there is a significant gap between the number of cybersecurity job openings and the pool of qualified candidates.
As per ISC², the global cybersecurity workforce gap currently stands at 3.12 million, which is a huge challenge.
This shortage severely impacts organizations’ ability to effectively defend against cyberattacks.
Various educational programs, professional training, and certifications have been designed to prepare individuals for cybersecurity roles.
Moreover, companies are now turning to automation and AI to fill the gap, but the need for skilled professionals remains high.
Empowering Visionary Technologies with SPDLoad.
16. Deception Technology
Deception Technology presents a groundbreaking approach to cybersecurity that utilizes decoys and traps to deceive attackers and detect breaches early.
By creating a controlled environment mimicking an organization’s IT assets, deception technology can divert attackers from valuable resources and collect intelligence on their tactics.
This proactive security measure is gaining popularity due to its ability to detect sophisticated threats that can bypass traditional security controls.
The global market for deception technology is expected to grow, driven by its effectiveness in improving detection capabilities and reducing attack response time.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity trends demand stronger defenses against sophisticated threats, with individuals and organizations staying vigilant and proactive in their security practices.
The digital landscape is evolving quickly, meaning individuals and companies must be alert and take proactive measures to protect their digital assets.
For those working in this field, staying up-to-date with these IT trends is essential to ensure the safety of sensitive data.