What is Cloud Migration? Benefits and Challenges
- Updated: Feb 02, 2026
- 12 min
According to the McKinsey report, in 2025, most companies aimed to spend $8 out of every $10 on cloud services. These include private cloud, IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
Reaching this goal will need a lot of work from both businesses and cloud providers.
Cloud migration involves moving applications, infrastructure, data, and other software objects to a cloud environment.
Usually, companies move apps, services, IT resources, and data centers from on-premises servers to the public cloud.
They can transfer the entire infrastructure or just a part of it.
However, cloud migration can also include transferring data and applications from one cloud provider to another.
It is possible to migrate systems as they are or to continue optimizing and modernizing them if necessary.
It is also possible to migrate on-premises servers to the cloud and vice versa.
Cloud migration service is a complex process, and it contains several stages.
These are the project discovery phase, planning, migration, optimization, and maintenance phases.
In this article, we discuss what a successful cloud migration takes.
Explore the advantages of cloud-based app development to improve app performance and accessibility.
Transform your ideas into reality with our dedicated development team — contact us to get started today!
What Is The Cloud Migration?
Cloud migration means moving your data, apps, or IT systems from local servers to the cloud environment. It helps businesses store and access information online instead of using on-site hardware. This makes scaling, updates, and security easier.
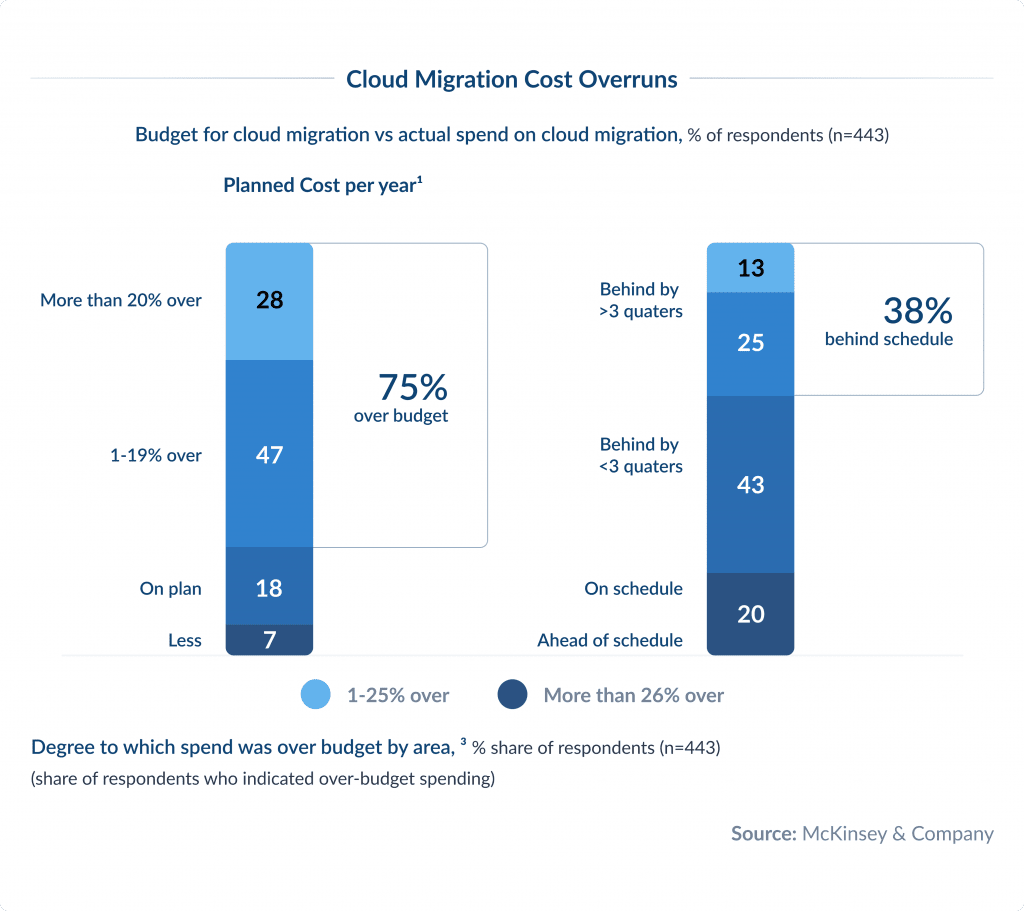
Research from McKinsey & Company shows that although many companies are moving more of their workloads to the public cloud, poor coordination during the cloud migration process is causing problems.
On average, companies are spending 14% more than they planned each year on cloud migration. 38% of companies have had delays of more than 3 months in their migrations.
These extra costs add up big time globally.
Over 3 years, the extra spend on cloud migration is over $100 billion. If these issues aren’t addressed, the costs will result in over $500 billion in lost shareholder value over the same period.
But careful planning and understanding of your existing IT landscape can reduce migration costs by up to 30%.
Before you move to the cloud, you should choose the right cloud approach for your business and technical needs. 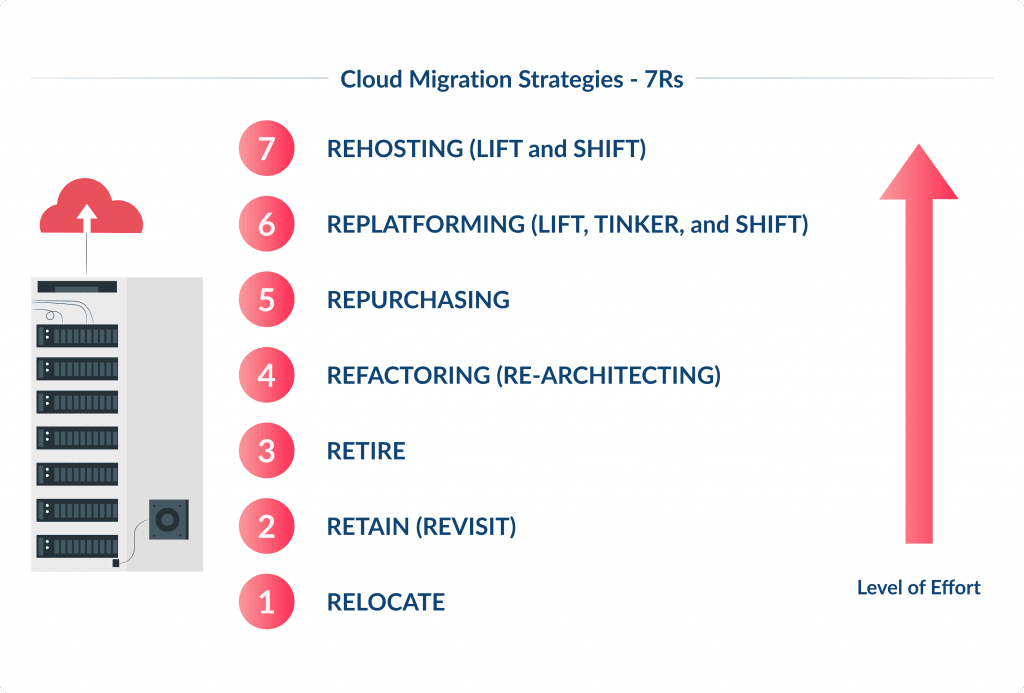
Here are seven cloud migration strategies, also known as “7 Rs”:
- Rehost (Lift and Shift) – move applications from on-premises to the cloud with minimal changes. This is the quickest migration path and suitable for applications that don’t need to change to run in the cloud.
- Replatform (Lift, Tinker, and Shift) – make a few tweaks to take advantage of cloud benefits without changing the core app architecture. This might be moving to a managed database service or using a cloud load balancer.
- Repurchase – move to a different product, usually a SaaS solution. Learn more about how to build a SaaS product.
- Refactor (Re-architect) – re-architect and re-develop applications to take full advantage of cloud features. This is the most beneficial but takes the most time and effort.
- Retire – identify applications that are no longer useful and can be turned off. This reduces costs and complexity in the migration process.
- Retain (Revisit) – keep some applications on-premises, at least temporarily, usually because they’re not ready to be migrated. This might be for applications with dependencies that can’t be moved or systems that require high security.
- Relocate – move entire data centers to the cloud without changing the applications.
Benefits of Cloud Migration
Many companies adopt cloud computing to stay agile, reduce costs, and improve performance. Here are some of the key benefits of moving to cloud for your business:
1. Cost Savings
One of the main benefits of migrating to the cloud infrastructure is that it lets you pay only for what you use. You avoid big upfront investments in hardware and software licenses, maintenance, and data centers.
For example, Netflix moved to AWS to scale quickly without massive IT expenses. Many startups also choose cloud providers to keep initial costs low and flexible. Here is a clear definition of what is a startup and what is not.
The streaming market is booming. Discover how to start a streaming service like Netflix and claim your space.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud computing platforms let you scale your resources up or down based on demand. This means you don’t need to overinvest in infrastructure during low seasons. Shopify, for instance, handles Black Friday traffic spikes smoothly thanks to its cloud setup. With the cloud services, growing companies can expand without IT limits holding them back.
3. Better Performance and Speed
Another business benefit of cloud migration is better performance across the globe. Cloud providers use global data centers, which often makes cloud applications and websites run faster for users around the world.
Automatic updates and optimized resources mean better performance without manual tweaks. Pinterest shifted to Google Cloud to handle its rapid user growth and keep its app fast. Cloud hosting also reduces downtime risks.
4. Enhanced Security
Top cloud providers invest heavily in data security, often more than most companies can afford in-house. This includes advanced encryption, constant monitoring, and compliance with global security standards. For example, Capital One migrated to AWS and improved its security posture with real-time threat detection. While no system is hack-proof, the cloud environment often offers better protection than local servers.
5. Security And Compliance
Moving to the cloud benefits security and compliance. Cloud providers often offer advanced security features that comply with industry regulations.
This results in a more secure environment than many on-premises solutions. For instance, if a healthcare provider migrates their telehealth app to the cloud, it can benefit from robust security measures and compliance with HIPAA regulations.
This step ensures that patient data remains secure and private. Plus, this is critical to maintain customer trust and avoid legal issues.
Types of Cloud Migration
Here are the main types of cloud migration:
On-Premises to Public Cloud Migration
This is the most common type of migration. It means moving your applications, data, and workloads from an on-premises data center, your company’s own servers, to a public cloud-based service provider like AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud. Businesses often choose this option to reduce infrastructure costs, improve scalability, and boost flexibility.
On-Premises to Hybrid Cloud Migration
In this case, companies move some of their workloads to the cloud while keeping sensitive data or critical systems in their on-premises data center. A hybrid cloud approach allows businesses to balance security, compliance, and scalability. For example, financial services often store client data on-site while running customer-facing apps in the cloud.
Cloud-to-Cloud Migration
Sometimes, businesses switch from one public cloud provider to another for better pricing, performance, or services. This type of migration helps avoid vendor lock-in but requires careful planning to move data, applications, and services between different data center infrastructures.
Reverse Cloud Migration (Cloud Exit)
Also called “cloud repatriation,” this is when companies move data or apps from the public cloud platform back to their on-premises data center or private servers. This may happen due to rising cloud costs, security concerns, or regulatory requirements.
Key Cloud Migration Steps
To ensure you are well-prepared for the cloud migration journey, follow a clear strategy. All aspects of the transition should be thoroughly planned and executed. Here are the key steps of the cloud migration process:
Step 1: Assess the existing system
Analyze your existing apps, data, and infrastructure. Decide what you’ll move, what needs upgrading, and what can stay on-premises. This helps avoid moving unnecessary or outdated systems.
Step 2: Identify The Business And Technical Drivers
Next, identify the business and technical drivers for the migration.
You need to understand the motivations behind moving to the cloud. These are cost savings, scalability, performance improvements, or security enhancements.
Learn about the most impactful cybersecurity trends to safeguard sensitive data and prevent breaches.
It can help you prioritize the migration efforts and align them with the company’s goals.
For instance, an HRMS business looking to expand globally might prioritize applications that benefit most from cloud scalability and availability.
HRMS can revolutionize your workplace. Learn what a human resource management system is and why it matters.
Step 3: Validate The Migration Strategies
After identifying the drivers, validate the migration strategies.
Evaluate different approaches for moving applications to the cloud, such as rehosting, refactoring, or re-architecting.
Each application may require a different strategy based on its complexity, dependencies, and importance to the business.
Common strategies include:
- Lift and Shift (Rehosting): Moving apps as they are.
- Refactoring: Modifying apps to fit the cloud better.
- Rebuilding: Redesigning apps from scratch for the cloud.
Step 4: Choose a Cloud Provider
Pick a trusted cloud service like AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud. Consider factors like pricing, security, compliance, and support.
Step 5: Prepare Data and Applications
Back up your data and check compatibility. Test the apps in a staging environment to fix bugs or performance issues before going live.
Step 6: Execute the Cloud Migration
Move your apps and data based on the chosen strategy. This might happen in phases or all at once, depending on the business risk.
Step 7: Test and Optimize
After migration, run performance tests, check security settings, and optimize resource usage. Make sure everything works as planned.
Step 8: Train Your Team and Monitor Performance
Ensure your staff know how to work with the new cloud setup. Set up monitoring tools to track performance, security, and costs.
Cloud Migration Checklist
Below is a comprehensive checklist covering key phases of cloud migration.
Pre-Migration Planning
Define objectives & strategy
- Identify business goals (cost savings, scalability, performance, etc.).
- Choose a migration approach (Rehost, Refactor, Revise, Rebuild, Replace).
- Select cloud migration tools.
Assess the current environment
- Inventory applications, servers, databases, and dependencies.
- Classify workloads (critical vs. non-critical).
- Analyze performance benchmarks.
Choose a cloud provider & services
- Select a provider (AWS, Azure, GCP, etc.).
- Decide on IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS models.
- Evaluate compliance and security requirements.
Cost estimation & budgeting
- Estimate cloud costs using pricing calculators.
- Plan for licensing, storage, and network expenses.
Security & compliance review
- Ensure data protection (encryption, access controls).
- Verify compliance with regulations (GDPR, HIPAA, etc.).
Create a cloud migration team
- Assign roles (cloud architects, security experts, DevOps, stakeholders).
Migration Preparation
Design cloud architecture
- Plan VPCs, subnets, security groups, and IAM roles.
- Define backup and disaster recovery strategies.
Data migration strategy
- Choose data transfer methods (direct transfer, VPN, AWS Snowball, etc.).
- Schedule migration during low-traffic periods.
Application readiness
- Identify refactoring needs for cloud compatibility.
- Test applications in a staging environment.
Network & connectivity setup
- Configure VPN or Direct Connect for hybrid cloud solution setups.
- Set up DNS and load balancing.
Backup & rollback plan
- Take full backups before migration.
- Define rollback procedures in case of failure.
Execution & migration
Pilot migration (Test Phase)
- Migrate non-critical workloads first.
- Validate performance, security, and functionality.
Full-scale migration
- Migrate remaining workloads in batches.
- Monitor for errors and performance issues.
Data synchronization & cutover
- Sync live data before final cutover.
- Schedule downtime (if needed) and notify users.
- 4. Post-Migration Validation
Testing & validation
- Verify application functionality and integrations.
- Conduct security and penetration testing.
Performance optimization
- Monitor resource usage (CPU, memory, network).
- Adjust auto-scaling and cost-saving measures.
User training & documentation
- Train teams on new cloud tools and processes.
- Update documentation for future reference.
Decommission old systems
- Shut down legacy systems securely.
- Archive data if required.
Ongoing Management
Continuous monitoring
- Use cloud-native tools and cloud resources(AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor).
- Set up alerts for anomalies.
Cost management & optimization
- Review cloud spending regularly.
- Implement reserved instances or spot instances for savings.
Security & compliance audits
- Regularly audit access controls and permissions.
- Ensure compliance with evolving regulations.
Scaling & updates
- Automate scaling based on demand.
- Keep applications and services updated.
Disaster Recovery In Cloud Migration
When you move to the cloud, having a solid disaster recovery plan is a must. Disaster recovery means having strategies and tools in place to restore your critical data and applications fast if something goes wrong, like a cyberattack, system failure, or natural disaster. The goal is simple: keep your business running with minimal downtime and data loss.
The cloud, especially when you use public or private cloud providers, makes this easier thanks to flexible storage, automated backups, and robust disaster recovery capabilities that traditional data centers often can’t match. Here’s how it works:
- Data backup
You regularly create and store backups in different locations. That way, even if your primary data is lost, you can quickly recover from another source. - Redundancy
Cloud providers offer built-in redundancy, meaning they duplicate your systems across different servers or regions. If one fails, another picks up the load, often without you noticing. - Failover mechanisms
With automatic failover, your systems switch over to backup servers or environments seamlessly when a failure occurs. This helps avoid major service interruptions. - Testing and drills
It’s not enough to have a plan; you need to test it. Regular drills help your team know what to do and make sure the disaster recovery plan actually works when it matters.
In short, cloud migration gives you access to disaster recovery options that are often more reliable and cost-effective than traditional data centers. It’s one more advantage of moving to cloud.
What are the Challenges in Cloud Migration?
Knowing the benefits of moving to the cloud, businesses should also be aware of common pitfalls. These include:
1. Lack of a Clear Migration Strategy
Without a well-defined plan, organizations may choose the wrong migration approach. For example, they might move applications as-is (lift-and-shift) when they need optimization (refactoring). This can lead to inefficiencies, higher costs, and poor performance in the cloud.
2. Unexpected Costs
Another common pitfall is cost overrun. Many businesses underestimate cloud expenses, such as data transfer fees, storage costs, and licensing. Without proper cost monitoring, cloud migration spending can quickly spiral out of control.
3. Legacy System Compatibility
Not all apps are ready for the cloud. Legacy systems might need refactoring or rebuilding, which adds time and complexity.
Older applications designed for on-premises infrastructure may not work well in the cloud. Some may require significant modifications or even full redevelopment. This adds time and cost to the cloud migration process.
4. Data Migration Difficulties
Moving large volumes of data to the cloud can be slow and complex, especially if the business requires minimal downtime. Data integrity and security must also be maintained during the transfer.
Additionally, transferring sensitive data poses risks such as breaches or compliance violations. You need strict access controls, encryption, and to follow regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
5. Network and Performance Issues
Applications that rely on low-latency connections may suffer if network performance is inconsistent in the cloud. Poorly configured cloud networks can also lead to bottlenecks.
6. Application Dependencies
Many applications depend on other systems or databases. If these dependencies are not properly migrated or reconfigured, applications may fail or behave unexpectedly in the cloud.
7. Vendor Lock-In Risks
Using proprietary cloud services can make it difficult to switch providers later. Organizations may become overly dependent on a single cloud vendor, limiting flexibility.
8. Security Risks
Misconfigured cloud settings (such as open storage buckets or weak access controls) can expose sensitive data. Ensuring security in a shared cloud environment requires careful planning.
9. Identity and Access Management (IAM) Complexity
Managing user permissions across cloud and on-premises systems can be difficult. Overly permissive access or poorly managed roles can create security risks.
10. Resource Scaling Challenges
If cloud resources are not properly scaled, businesses may overpay for unused capacity or face performance issues during peak demand.
11. Skill Gaps and Training Needs
Many IT teams lack experience with cloud technologies, requiring training or hiring new talent to manage the cloud environment effectively.
12. Resistance to Organizational Change
Employees accustomed to traditional IT systems may resist cloud adoption, slowing down the migration process.
13. Shadow IT and Unauthorized Cloud Use
Without proper governance, employees might use unauthorized cloud services, creating security and compliance risks.
14. Post-Migration Cost Management
After migration, ongoing monitoring is needed to optimize costs, such as shutting down unused instances or selecting cost-effective storage options.
15. Downtime and Business Disruption
Poorly planned migrations can lead to unexpected outages, disrupting business operations and customer access.
How to overcome these challenges?
- Plan carefully with a clear roadmap and phased approach.
- Train employees on cloud best practices.
- Monitor costs using cloud cost management tools.
- Test thoroughly before full migration.
- Implement strong security and compliance controls from the start.
Keen To Get Started With The Cloud Migration Process?
As of 2021, companies managed about 35% of their cloud needs with their own staff. By the end of 2024, they hope to increase this to around 50%.
However, there is already a shortage of skilled cloud professionals, and this increased demand will make it even harder to find the right talent.
To address this gap, some companies use external labor, like IT outsourcing partners.
However, problems can arise if the partnership is not well-structured.
For example, a global pharmaceutical company handed over its cloud migration almost entirely to SIs without having strong in-house development expertise.
Because the SIs were paid based on the time they spent rather than their performance, they had little incentive to complete the cloud migration process quickly.
As a result, some projects took longer and cost more than expected.
Partnering up for app development? Here’s what to keep in mind for a productive app development partnership.
Aside from change management, spending on SIs was one of the most common reasons for cost overruns.
Hence, value creation is a key metric that a reliable cloud service provider should focus on when assisting businesses with cloud migration.
Are you looking for a reliable partner to get started with your cloud migration project?
We are here to help you out.
Our team helps companies of all industries and sizes solve their infrastructure problems through cloud migration.
If you want to learn more about the overall migration process, cloud technology in general, or AWS cloud services, feel free to reach out.
Discover the strengths and weaknesses of Digital Ocean, AWS, and Google Cloud to find your ideal match.
We are here to review your circumstances, needs, and goals to outline the best approach for you, including clear steps to achieve it. Our specialists will be with you every step of the way to ensure your cloud data migration significantly boosts your operations.
Let’s chat!