Top 8 Trends in Digital Transformation in Insurance
- Created: Sep 27, 2024
- 18 min
Technology advancements propel multiple industries.
We can already see how AI changes the way we generate content, use services, and consume information. To navigate the world of AI, it’s important to know the language. Our AI glossary offers concise explanations for key terms.
The insurance sector is not an exception.
The sector is under pressure, and people are shifting their spending to tap into new technological frontiers.
Insurtech startups innovate and create new digital solutions to make it easy for people to find and buy insurance products in just a few clicks.
This is a complex and challenging process, but in order to succeed, insurers need to anticipate and embrace change.
What lies ahead as digital becomes the new normal, and what should insurance leaders prepare for?
Let’s explore some trends in digital transformation in insurance.
We believe they will shape the insurance sector in the next few years.
We empower insurance innovation through custom apps
The Need for Digital Transformation in the Insurance Industry
Before we dive into the trends, let’s focus a little bit on the insurance industry market overview.
According to Technavio report, the insurance software market is expected to grow by $7.54 billion by 2028.
The CAGR is a steady 7.81%.
The market growth relies on multiple factors.
These are government regulations mandating insurance in developing countries, increased demand for insurance due to uncertain catastrophic events, and growth of insurance services in emerging markets.
In developing countries, government regulations are strict and individuals and businesses are forced to buy insurance, which drives growth.
Moreover, unpredictable catastrophic events like natural disasters or pandemics make insurance necessary, and individuals and businesses are looking for financial protection.
This increased awareness of risk mitigation further boosts insurance adoption. 
Key Digital Transformation in Insurance Trends for 2024 and Beyond
There are multiple trends that shape the digital transformation in insurance.
In this article, we explore 8 of them.
These are:
- The growth of low-code and no-code development practices
- The increasing popularity of headless tech
- Hybrid cloud architecture is on the rise
- The rise of customer self-service
- The growth of usage-based insurance
- Adoption of sensor-based wearables
- Predictive analytics growth
- Increased focus on algorithmic risk assessment
We will dive into each of these trends and highlight their importance, challenges, benefits, and opportunities.
Curious about where app development is headed? Our application development trends guide has the answers. 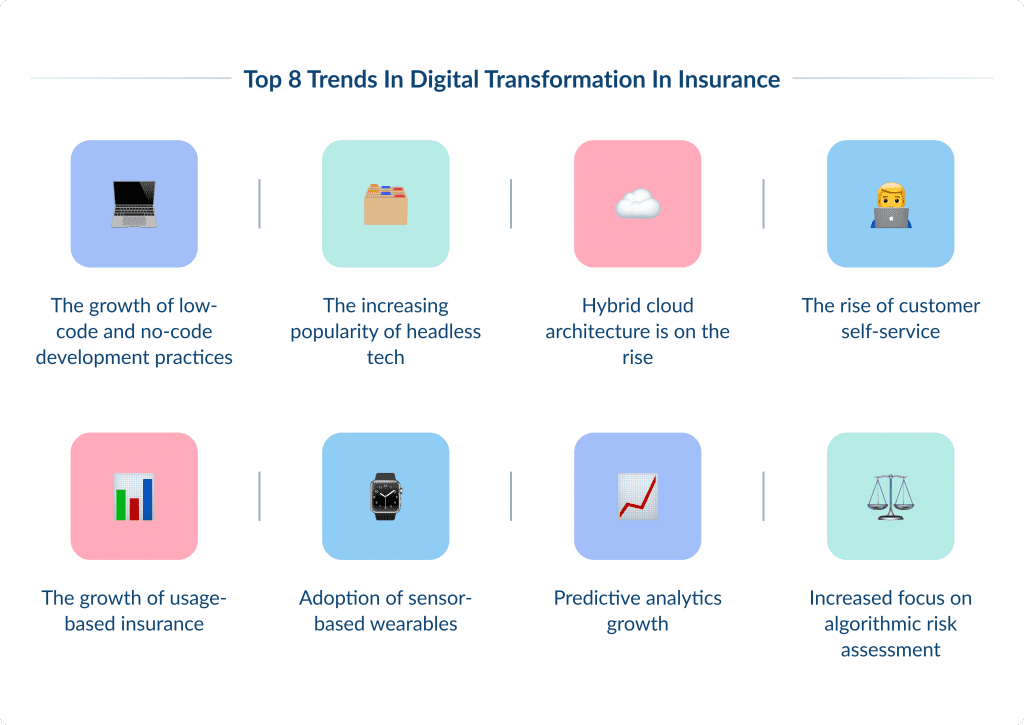
The Rise of Low-Code/No-Code Development
Low-code and no-code platforms are modern digital innovation solutions.
They are used across multiple industries and the insurance industry is no exception.
Using low-code and no-code solutions, users can create entire applications with minimal to no programming skills.
The apps are created simply through graphical user interfaces and configuration.
This is much cheaper and faster than traditional programming.
There are many platforms offering low and no-code functions, for example Appian, Mendix, Microsoft PowerApps, OutSystems and Salesforce Lightning.
Insurance businesses can use low-code and no-code platforms to make their lives a little bit easier. 
For instance, to develop personalized customer portals and apps.
Insurance companies can use these platforms to automate routine tasks, such as insurance claims processing, underwriting, and customer service. See 15 examples of insurance companies.
What are some other advantages of adopting these low and no-code digital transformation solutions?
The responders of the Adacta State of Low-Code in Insurance survey highlight the following benefits:
- faster modernization of legacy platforms
- enhanced self-service and digital insurance experience
- improvement of the claims process and more
Explore them further: 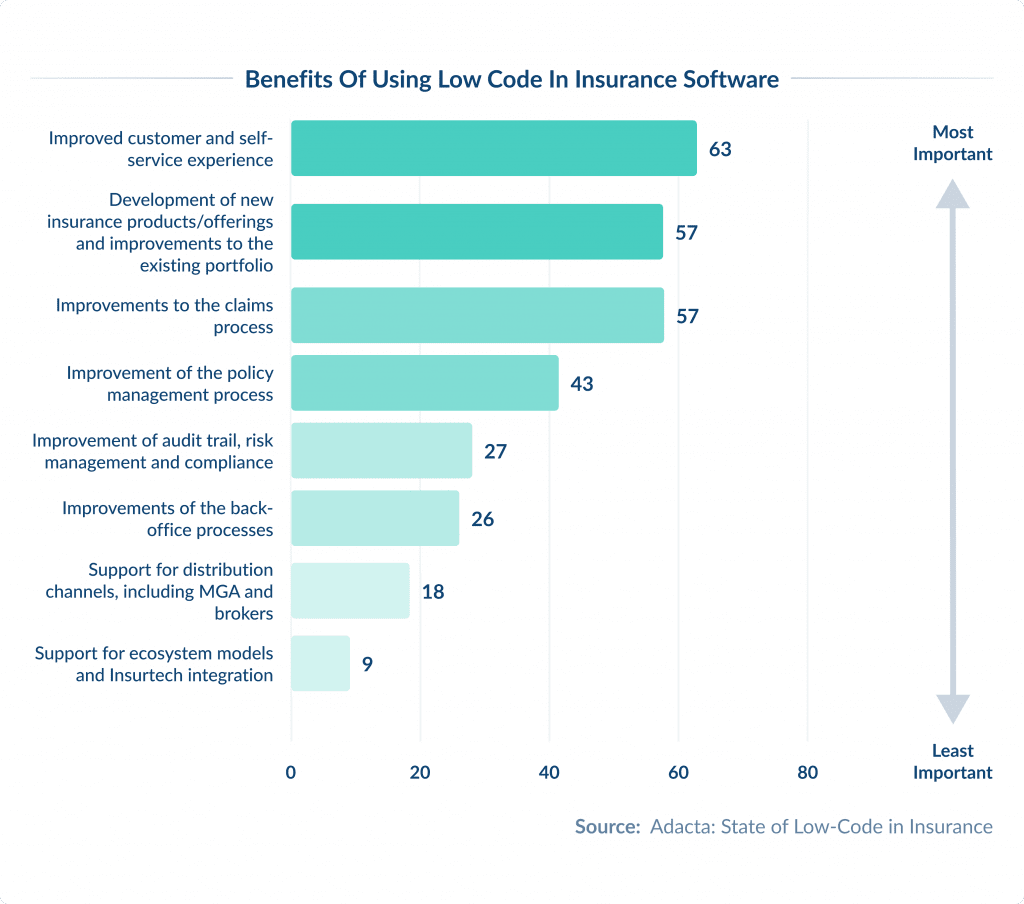
However, there are still challenges with the adoption of low-code insurance platforms among insurance companies.
Lack of support specific to the insurance industry, such as insurance-specific workflows, is the most common barrier.
Also, survey respondents consider support for ecosystem models and integration of insurance technologies are the areas that would benefit least from low-code development tools.
The Growing Usage of “Headless Tech”
Headless technology is a software architecture where the front-end (the “head”) and the back-end of a system are separated and function independently.
This separation enhances efficiency, performance, and presentation for various types of digital platforms.
Headless tech is a complementary trend that goes hand in hand with no-code tools for developing customer-facing front-ends.
Benefits of headless technology
Businesses can easily adjust and personalize their content based on specific customer preferences, behavior, and history.
Since the front-end is completely separated from the back-end, updates to the digital experience on the front-end can be executed swiftly and safely.
Unlike traditional systems where scaling often requires a complete overhaul of the entire architecture, headless technology allows each layer to be scaled separately.
This means that businesses can expand their user interface or enhance their data processing capabilities without necessarily having to adjust the other part.
Platfoкms like Amazon, Netflix, and Spotify already utilize headless tech to improve their user experience and service delivery.
Let’s take Netflix headless tech usage as an example.
Healdess tech allows the platform to adapt to customer demand and preferences.
With headless architecture they can update user experiences in real time from data collection.
This is especially important in mobile where customer expectations and behaviors change fast.
At the heart of every Netflix user’s homepage is a set of complex AI algorithms.
This is made possible by Netflix’s use of microservices, a part of headless architecture.
Microservices allows different parts of the Netflix app to work independently yet together to give a seamless and personalized customer experience.
Get a clear picture of your customers’ lifetime value with this CLTV calculator. It’s designed to make insights quick and simple.
Headless tech in insurance software
With headless technology, insurers can use data to make personalized recommendations for their customers.
Let’s say, you’re buying a car.
Using a headless tech, your insurer can offer you a personalized auto insurance quote based on your individual vehicle and driving history.
Another use case that is going to elevate customer experience is the use of chatbots.
With headless tech, insurers can design chatbots that seamlessly interface with their back-end processes. This way, there will provide their clients with quicker and more efficient service.
One more use case is mobile apps.
Insurers are trying to cater to customer demand for a smooth mobile experience.
Headless tech can be helpful in this situation as it allows the development of mobile apps that simply interface with insurers’ back-end systems.
This will allow customers to view their insurance information and file claims from anywhere.
These are just few use cases but we can already see that the market demand is there.
So now, it is time for actions.
Hybrid Cloud Architecture is on the Rise
The insurance software market is mainly operated by large organizations.
These leading insurance companies consider data privacy and security a priority. Which is good for their customers.
However, these organizations focus more on functionality than on cost-effectiveness.
The high security and data privacy of the on-premises deployment model is driving the market growth.
The on-premises insurance market segment was evaluated at $9.93 billion in 2018.
The market growth is attributed to multiple unique properties of this deployment model.
First, is the fact that in case of on-premise, organization takes full control over the in-house server, IT infrastructure, IT team, and intranet.
Another reason is that on-premise software is more convenient in areas where the internet connection is poor, for example in rural areas. In this case, cloud software is not an option.
Also, unlike cloud-based software, the on-premise software used by insurance companies controls data security and confidentiality, as well as compliance with government regulations, rules and protocols.
Explore our guide to cybersecurity trends and see what your organization needs to stay secure.
In our tech-savvy and thread-filled world, enterprises prioritize their risk management above everything else.
Hence, the factors we’ve mentioned above will more likely continue drive the growth of on-premises software in insurance space.
Learn about effective bot attack prevention strategies to safeguard your site and data.
On-premises: These solutions involve installing software and managing data within the organization’s infrastructure.
They prove a high level of control but require significant maintenance and resource costs.
SaaS-based: These are cloud-based solutions.
They offer access from anywhere with an internet connection.
Explore the advantages of cloud-based app development to improve app performance and accessibility.
SaaS solutions reduce infrastructure costs, provide automatic updates, and are known for their scalability.
It makes them popular among companies seeking flexibility and efficiency in software deployment.
If you’re deciding between software models, this comparison of the ASP model vs SaaS model can help you choose. 
The Rise of Customer Self-Service Portals
Another driver of digital transformation in insurance is self-service portals.
Let’s get into it.
Self-service portals and other digital channels allow insurers to create a new approach to insurance products.
A Harvard Business Review survey found 81% of insurance customers choose self-service portal as one stop solution.
Customers expect to resolve their queries as quickly and effortlessly as possible and no human communication.
Forrester survey found 70% of B2B buyers prefer to buy insurance related products from website rather than reaching out to sales reps.
Considering this, insurance providers that have self-service portals earn 30% more than those without.
Wondering how long it will take to launch? Check out the average time to create a website for a realistic timeline. 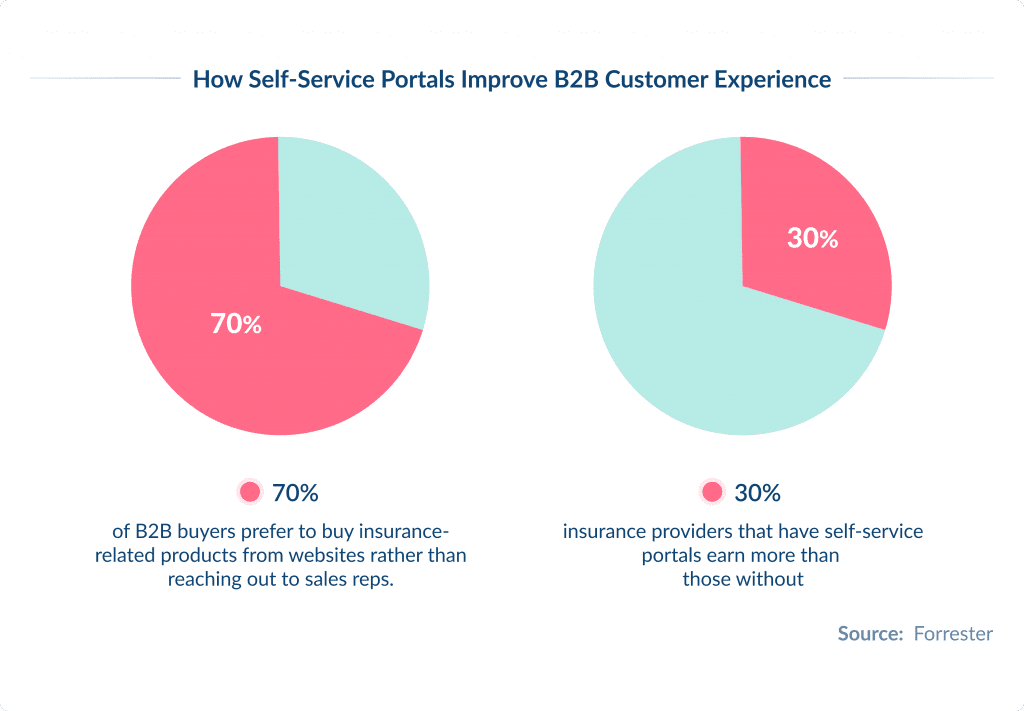
Growing Adoption of Sensor-Based Wearables
There is an emerging trend in the insurance industry to incorporate wearables into customer engagement metrics.
Fitness and health data can be tracked by wearable devices, such as smartwatches and small portable computers.
These sensitive customer data can be used to customize and personalize health insurance contributions.
For example, those individuals with a healthy lifestyle can receive a reduction in their contributions to be paid.
Based on the most recent data, insurers can suggest or develop modified products to suit customer lifestyles and maximize company profits while minimizing risks.
It is important to note that wearables’ features can only be used if they are integrated into online offerings.
The insurance software can utilize the data collected to conduct both individual and mass scale analysis in order to redefine the product portfolio and redesign clauses for claims and disbursal.
The factors we’ve mentioned above will most likely fuel the growth of sensor-based wearables.
BMC research on adopting wearables to customize health insurance contributions has also highlighted the barriers to such adoption.
The most concerning are regulation barriers. These are issues connected with privacy and data protection.
Another barrier is the risk of inaccurate measurements and application errors, which are issues for which the users are responsible.
The next barrier concerns insurers’ lack of technological know-how to use wearable data appropriately.
Other challenges mentioned in the research are that wearable data is not suitable for individual contributions and that contribution customization is not compatible with the solidarity principle of insurance.
Less important barriers are lack of people accepting to wear wearables in public, bad cost-benefit of individual contributions, no access to wearables and fear of higher insurance contributions because of suggested unhealthy behavior. 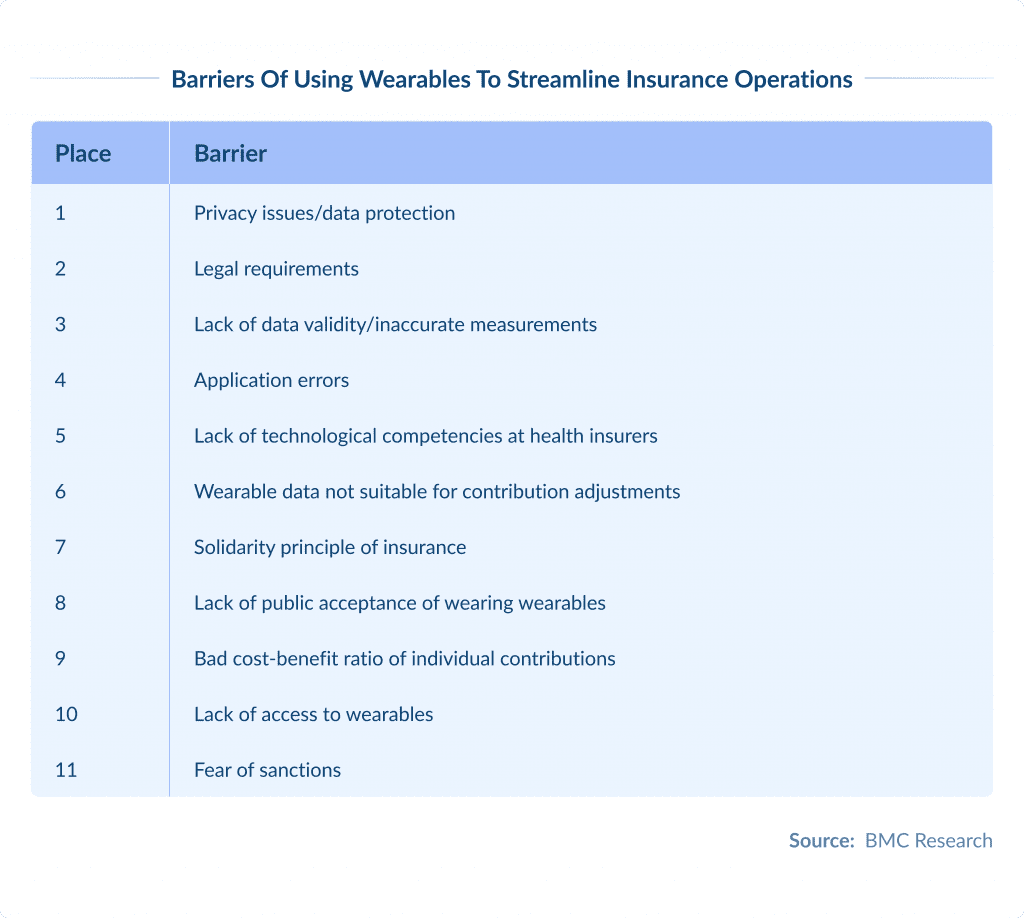
Explore our SaaS services today
Usage-Based Insurance is Getting Popular
For insurance companies looking to innovate, car insurance app development is a game-changer in customer engagement.
Usage-based insurance (UBI) is usually linked to car insurance.
Here’s how it’s different from traditional car insurance.
Traditional car insurance sets premiums based on general factors like the driver’s age, gender, location and driving history.
UBI uses telematics to monitor driving behavior.
To monitor driving behaviour a device is installed in the vehicle or a smartphone app is used.
The device collects data on various driving metrics such as speed, acceleration, braking, mileage and even the time of day the vehicle is used.
Some UBI programs offer real-time feedback through apps or online portals.
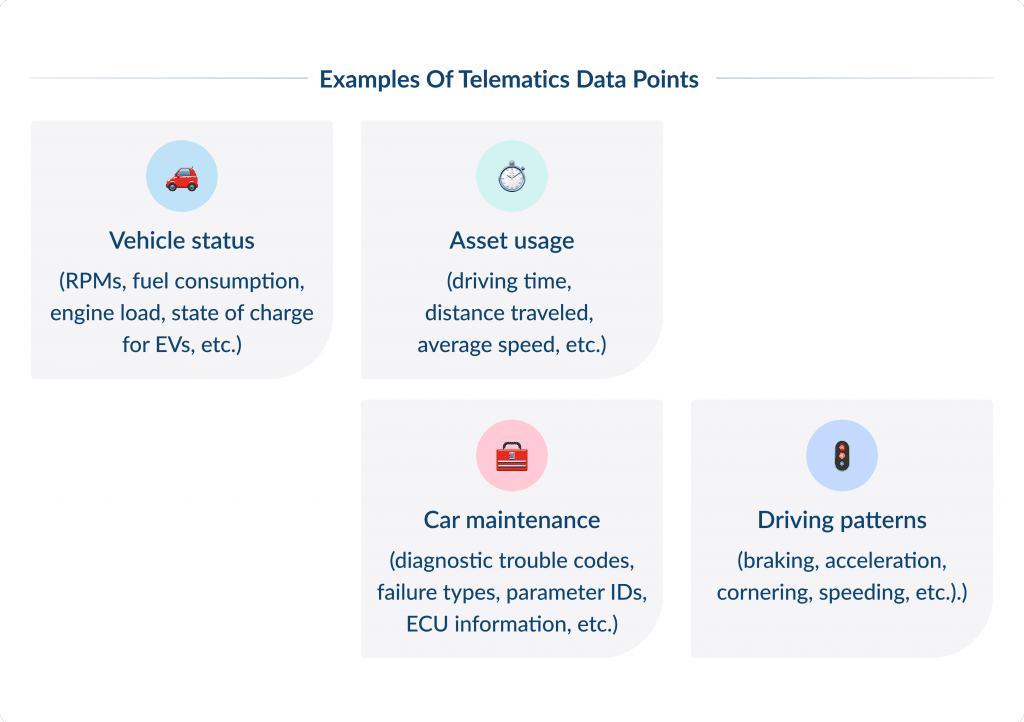
Examples of telematics data points include:
- Vehicle status (RPMs, fuel consumption, engine load, state of charge for EVs, etc.)
- Asset usage (driving time, distance traveled, average speed, etc.)
- Car maintenance (diagnostic trouble codes, failure types, parameter IDs, ECU information, etc.)
- Driving patterns (braking, acceleration, cornering, speeding, etc.)
This enables drivers to monitor how their driving behavior affects their insurance costs.
This information can prompt drivers to adjust accordingly, leading to more safe and mindful driving.
With the increasing penetration of internet-connected cars making it easier to collect data on vehicles and drivers, usage-based insurance is estimated to show steady growth in the coming years.
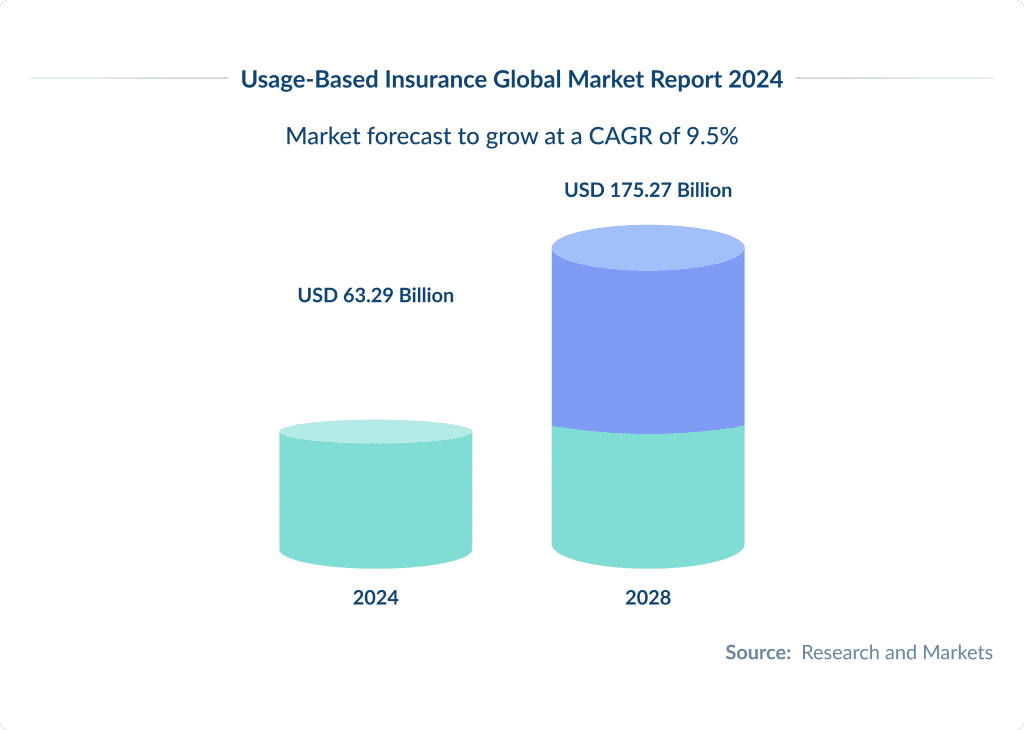
The global usage-based insurance market was estimated $30.6 billion in 2023.
It is predicted to grow to $80.7 billion by 2028, with a staggering 21.4% CAGR of 21.4%.
Usage based insurance offers multiple benefits.
These are:
- personalized offerings
- lower premiums
- greater control compared to conventional insurance
A telematics system provides detailed information on how a car performs over the course of its lifetime.
Meanwhile, insurance companies use this data to create personalized rates and offers for their customers.
Overall, UBI also offers a compelling value proposition that can attract tech-savvy and cost-conscious consumers, giving UBI-embracing insurers a competitive edge.
North America was the leader in the usage-based insurance market in 2023, and many American insurance companies are jumping on the UBI bandwagon.
The Growth of Predictive Analytics Practices
In the insurance industry, predictive analytics is a technology that is able to identify the most probable outcomes based on data patterns.
This is not a new concept, of course. But with the rise of big data, AI and ML, predictive analytics has received an upgrade.
Since it is time consuming and manually complex to analyze data, it has also become virtually impossible as the amount of data has grown exponentially.
People and businesses generate immense amounts of data every single day.
Insurers need to collect, analyze, store, and conduct other manipulations with these data.
Predictive analytics for insurance automates all these activities and makes analysis faster and more accessible.
The predictive analytics trend can help every insurance company out there eliminate fraud, estimate financial risks, optimize business processes, and identify potential markets.
Example of using predictive analysis in the insurance industry
Deloitte insurance industry survey highlights that artificial intelligence, paired with alternative data and advanced analytics, is poised to have a great influence on the entire insurance business value chain.
But only if its deployed correctly and those using it are trained properly.
These are many insurance businesses that have already increases their investment in conversational artificial intelligence or chatbots to improve communications among stakeholders and reduce wait times.
Artificial intelligence can also be used to process claims and identify suspicious patterns beyond traditional signals, as well as raise red flags about potentially fraudulent submissions.
Here is how it works in practice.
Mitsui Sumitomo Insurance, a Japanese insurance holding company, uses an AI-powered “agent support system” to better identify customer’s potential needsby analyzing internal and external data.
The support system delivered agents 860,000 individual and 80,000 corporate sales leads per month.
The agents’ productivity has increased between 20% and 130% compared to the conventional sales model.
This is a great example of how the use of artificial intelligence can improve predictive analysis.
Increased Focus on Algorithmic Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is a crucial aspect in insurance.
For many years, insurance companies have been using underwriting to assess risk price.
This risk assessment has always been a tedious process, with piles of documents to sift through. In the end, the final decision was mainly based on the undewriter’s experience and gut feelings.
With new technologies, risk assessment can be automated.
Let’s explore how it works.
Emerging technologies in risk assessment
Using modern technologies, including AI, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT), insurers are able to foster their risk assessment practices.
An Accenture study revelas that 82% of insurance executives expect that digital technologies will change the industry in the next 5 years.
If you want to stay ahead of the curve, now is a perfect time to start utilizing advanced technologies to level up your risk assessment.
According to Data Logistic and AI in Insurance Risk Management paper, the new generation risk management systems can become so powerful and disruptive that they are able to turn insurers’ business model upside down: from pooling to personalizing risks.
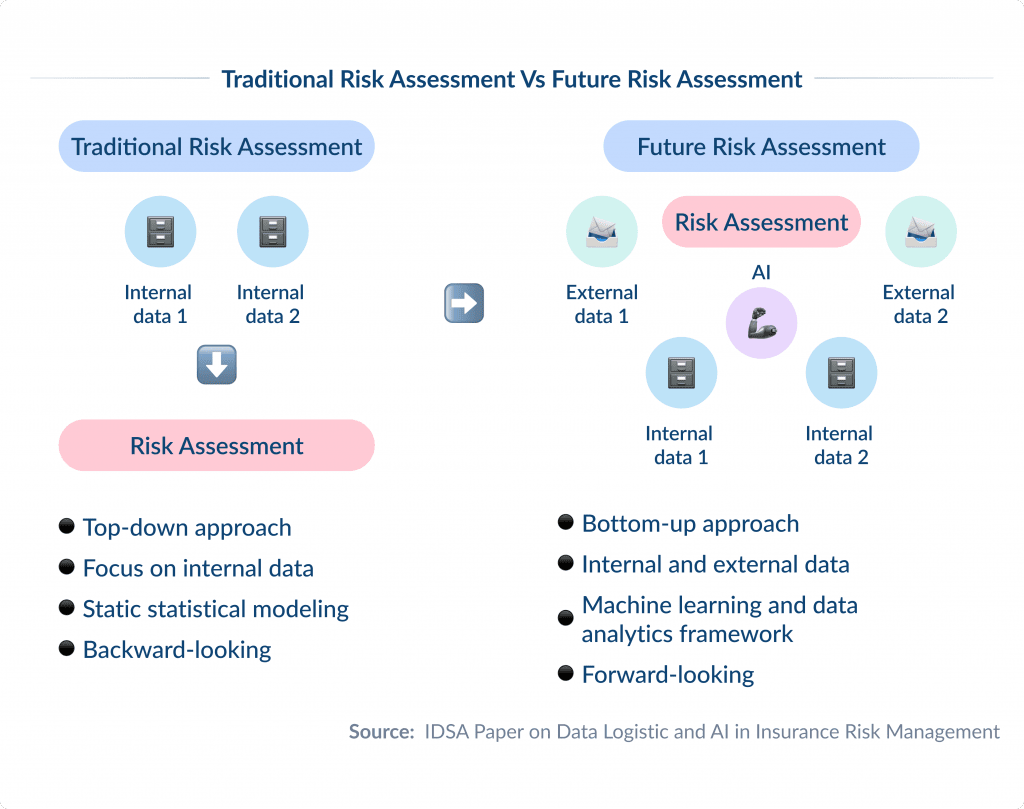
Insurance providers used to build on statistical and actuarial modeling of technical data to have been evaluate risks for pricing and hedging purposes.
You can see the traditional way of risk management on the left side of the scheme.
Based on various data sources within the company, such as claims and contract statistics, statistical modeling was applied to arrive at a certain risk statement.
The problem is that this process is static in nature and only focuses on historical data.
This is when modern technology disrupts the process.
Researchers predict that with AI methods, increasing tractability and emerging access to external data sources, this process can be turned upside down.
In future risk management, not only internal data, but more and more external data sources contribute to risk modeling.
This process is going to be more dynamic since data sources can be on- and off-boarded with little effort, while ML enables model-free risk estimation.
Given the importance of systemic methods in complex systems in general, the evolution of risk assessment will envisage a compositional, ML-based risk modeling approach of technical, behavioral etc. data, resulting in a more accurate and dynamic evaluation of risk.
Advanced, sophisticated AI-powered risk models, however, have not been largely observed yet in the insurance market.
AI adoption is low and slow due to methodological, data-centered and cultural issues.
So, this is still an emerging trend that required more research and innovations that will tackle the abovementioned challenges.
How is Digital Transformation Changing the Insurance Industry?
The insurance industry market is driven by the increasing adoption of insurance worldwide. Both in developing and advanced countries.
In fact, the insurance market in developed countries has become saturated.
This mainly happens because people become more aware of insurance services and their importance and are more likely to become early adopters of new technologies.
And developed countries have strict government rules for subscription to insurance. Life and health, property and casualty, travel insurance or special ones like marine and aviation.
Insurance solution providers are using artificial intelligence technology.
They manage outstanding claim reserves, develop policy management software and claims processing software.
And because of this digital transformation, the demand for customer-facing software is growing fast.
Demand is growing in developing countries.
No more traditional ways.
So, the market size and growth will increase many times during the forecast period.
The market is driven by increasing awareness of cyber risks, stricter regulations and continuous evolution of sophisticated cyber threats.
As businesses protect their digital assets, demand for full stack cybersecurity solutions is rising. 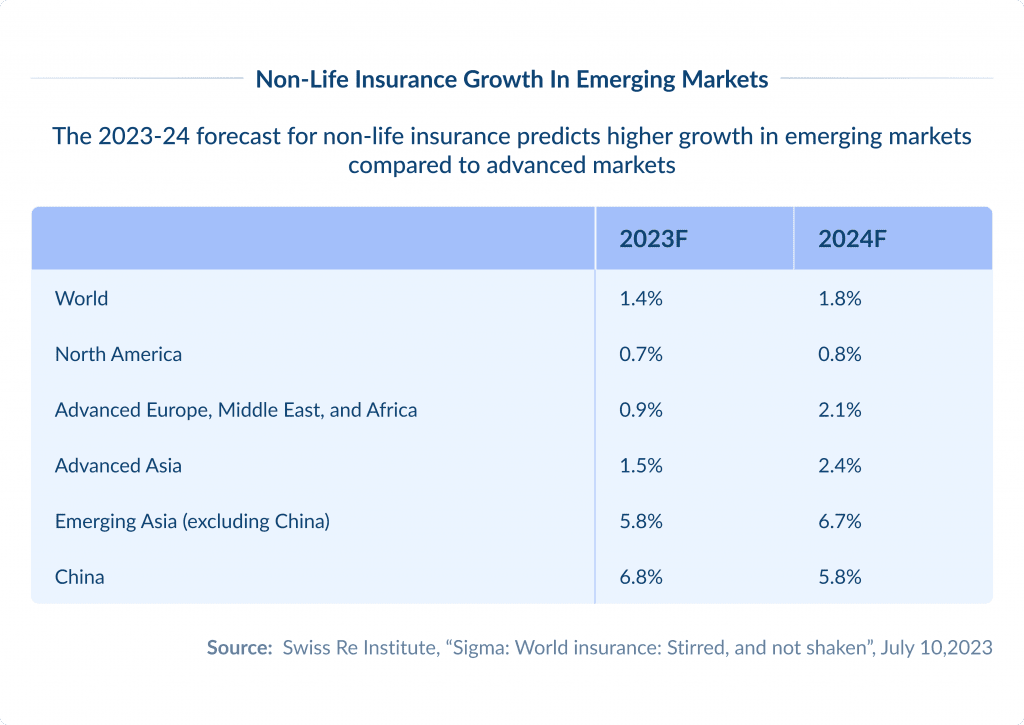
Best Practices to Implement Digital Transformation in Insurance
All the trends we’ve mentioned above are going to transform the insurance industry in the next few years.
To be prepared for this digital transformation, businesses need to start taking action now.
Let’s see what are some of the best practices for using digital tools to enhance insurance space. 
Leverage Digital Tools to Improve Insurance Operations
To prepare for the digital transformation of insurance and encourage agility, insurers must implement the right tools and find creative ways to optimize their operations.
You want to start with a clear and long-term roadmap for implementing technologies that will gradually transform your entire business.
Make sure your roadmap is workable and realistic. It should clarify why, how, when, and where to help you implement technologies in the most successful use cases.
For example, you can start off with AI chatbot implementation.
Deploy an AI chatbot to handle routine customer queries, guide them through the claim process, and provide necessary policy information.
This way, you can ensure 24/7 support that enhances customer experience without overworking your customer support team.
Another example of using digital tools to improve insurance operations is automated claims processing.
The introduction of AI-based insurance claims processing systems can significantly reduce the time required to evaluate and settle claims.
For example, Lemonade, a digital insurer, uses AI to process insurance claims in seconds by analyzing claim information and matching it with policy data.
Use our app development calculator to estimate app cost.
Focus on Customer-Centricity
Insurance solutions have a very specific target audience.
These are not the types of applications users will interact with daily.
They will use the app only when they need something.
This makes your “know your audience” task a little bit more complicated.
Simply because you won’t have ample opportunity to know their needs and expectations regarding digital experiences.
Additionally, people also don’t want to engage with your digital product more than that.
This fact comes into play when you consider upselling your users additional services. Sending them push notifications about new offers daily is probably not the best strategy.
However, sending them a push notification about travel insurance once their location changes to another country?
That is much more appropriate.
Or, let’s say the app detects that the user has bought a home (based on the data from connected financial accounts or information from partner services).
It can recommend home insurance options that are based on the needs of the brand-new house owner.
These tailored and personalized options are much better than bombarding your users with all types of insurance you have to offer.
Prioritize Data Privacy and Security
Since insurance companies deal with sensitive customer data daily, the data security aspect is paramount.
Users provide their personal data through digital products. Hence, they must trust the insurance providers.
That trust may come easily for established companies, but it’s also painfully easy to lose.
In fact, data breaches come with both financial and reputational losses. And the las one is extremely hard to recover from.
According to the survey from Technavio, users from countries with the highest insurance adoption rates (China, France, Japan, the UK, and the US) identify service, compliance, and innovation as their key purchasing criteria. 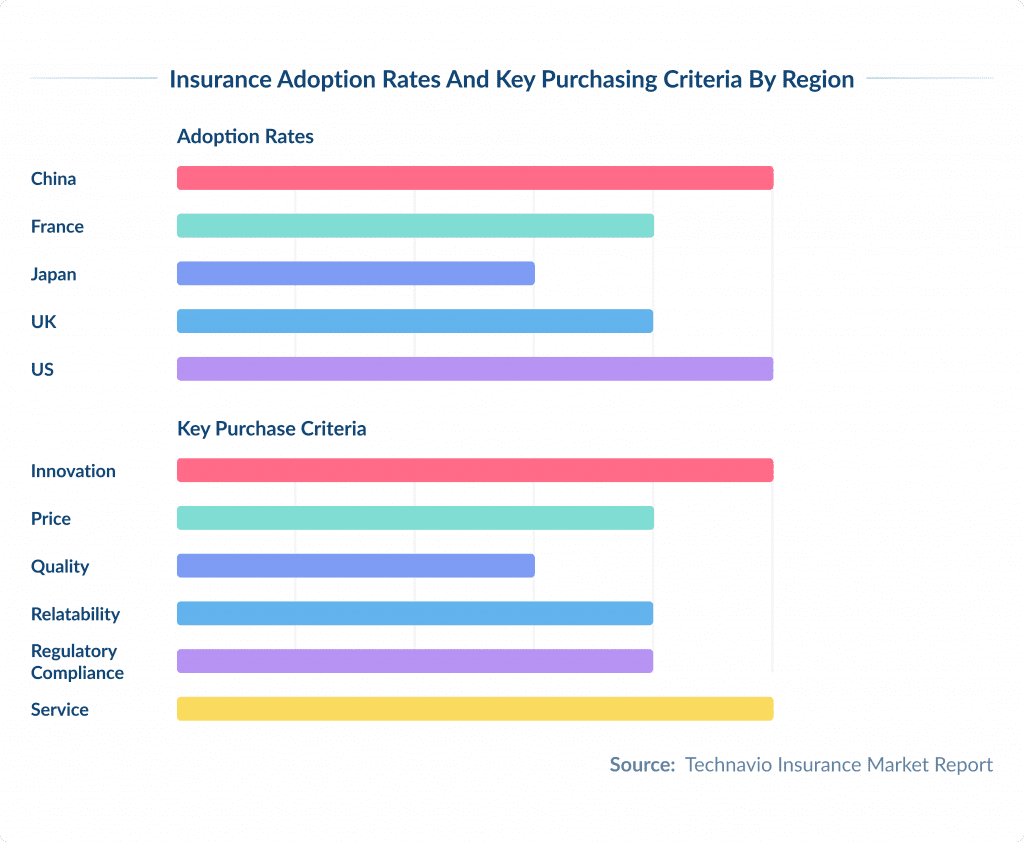
Keeping that in mind, insurance companies should be very careful how they design and develop their product.
Security must always play a critical role and be baked into every stage of the insurance software development process.
If you don’t have qualified specialists in-house, or struggle to hire them, consider hiring outside experts.
Outsourcing IT specialists will develop for you a secure and reliable solution based on your needs.
They will also test it thoroughly from a cyber security standpoint to make them bulletproof.
Discover the benefits of IT outsourcing and why it’s popular for scaling tech needs.
The Challenges Facing the Insurance Software Industry
Here are some of the challenges that may hinder the evolution of insurance software.
Data Privacy and Security
As we already mentioned, insurers keep a large amount of customer data within their systems.
This data is increasingly being stored in the cloud with the advent of digital transformation in the insurance industry.
This makes the data more vulnerable to malware and cyber-attacks.
That is why insurers need powerful security measures to protect their data. For example, multi-factor authentication and data encryption.
In addition, they must remain extremely vigilant against threats to their online platforms and customer data.
Resistance to Change
It can often be difficult to push employees to adopt new technologies and break their old habits and work methods.
Encouraging cultural change and implementing digital communication tools to support the transition can help.
In addition, create a more standardized environment and provide training so that employees can handle more challenging situations.
Create clear digital interfaces for different employees and test platforms to ensure they are as intuitive as possible.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Insurance is a highly regulated industry.
All companies must comply with numerous rules and regulations.
To do so, insurers maintain a large amount of data and paperwork, which makes it difficult to digitize processes.
Insurance businesses need to work closely with regulators to ensure that their data collection and overall transformation efforts are compliant with the relevant regulations.
Inefficient Data Management
The digital transformation of insurance companies is causing a sharp increase in the amount of data required and the different ways it can be processed.
While the data collected can open up more business opportunities, companies must address data quality and completeness issues, as different interpretations of data can lead to inaccurate results and forecasts.
Data management solutions and a comprehensive data management strategy can help insurers standardize their data and assign staff to consistently enter, store and manage data across the organization to drive business results. 
Spdload is Your Partner in Driving Digital Transformation in Insurance
This digital evolution comes with its challenges too.
It might be complicated to find a skilled workforce to implement digital innovations.
This can hinder technology adoption among insurance companies.
But it is possible to reduce this problem with the help of external specialists.
You can rely on Spdload in insurtech development.
We have been providing insurtech development services for over 10 years now and we know the industry inside out.
One of the latest insurtech solutions we’ve developed focused on making advanced industries safer.
They specialize in risk mitigation for semiconductor and data center projects, ensuring that everything runs smoothly and safely. 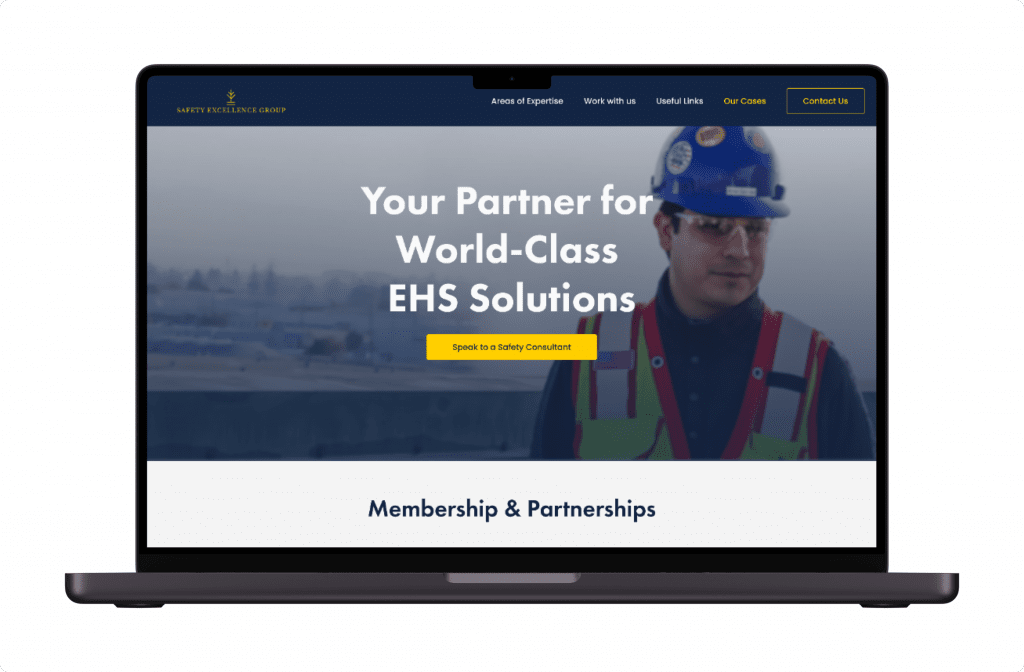
They work across many industries to improve safety and productivity.
Our team created a platform with separate roles for admins and consultants.
Admins can analyze this data through dashboards with graphs.
This is visualized through dashboards so admins can trend and make decisions.
ChatGPT integration lets consultants use a chatbot for safety queries, data analysis and insights, and pre-fill daily report forms.
Our solutions have advanced security, data management and is easy to use. Client is using it to improve safety and productivity in heavy industries.
Explore this safety solution development case study in more detail.
Want to start your digital transformation too?
Get in touch to chat about your project, create a plan and let’s get started!
Conclusion
Technological advances are driving the insurance market.
In addition, data analytics is increasingly being integrated into the core offering to generate insights, detect fraud and predict claims patterns.
The use of technology can improve the efficiency and security of document management.
This ensures that customers can keep their credentials and confidential information safe.
However, understanding and utilizing such high-tech innovations requires appropriate skills.
Companies should focus on making their software more user-friendly and improve customer experience as the market becomes more customer-centric.
In addition, customer satisfaction and brand trust increase if they can understand the process.
Thus, the data must be readable and understandable for customers to be useful to them.
If you want to dive deeper into insurance app development, make sure you check out our article on Top 7 Insurance App Trends.